Market Overview
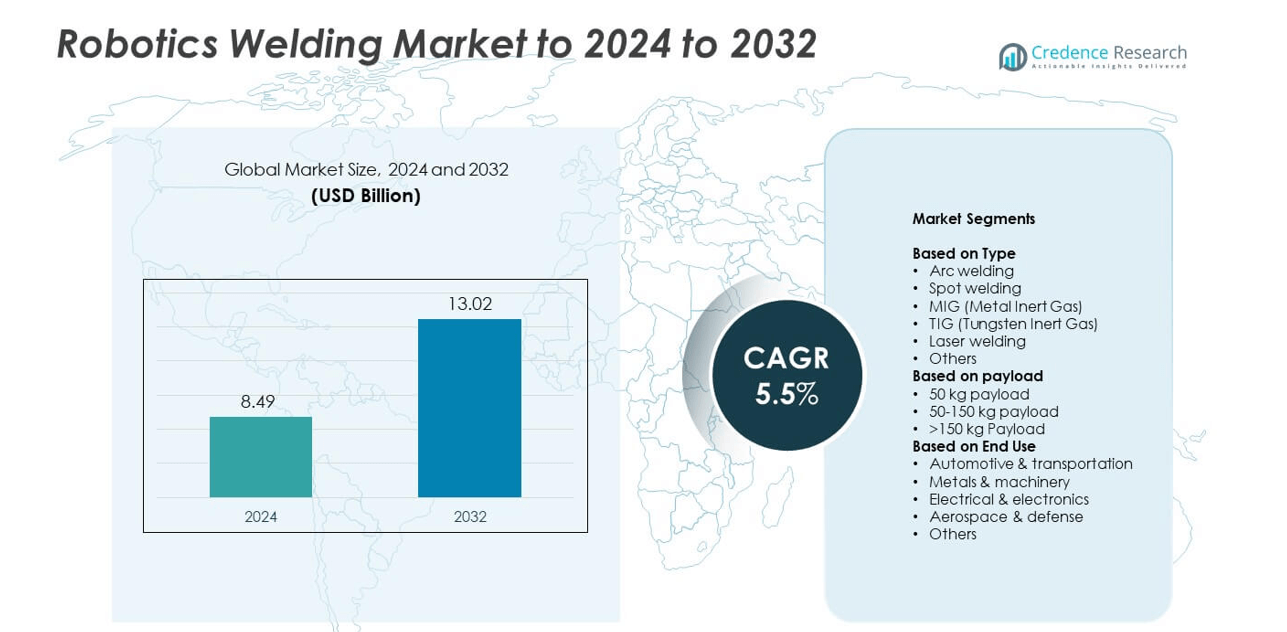
The robotics welding market size was valued at USD 8.49 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 13.02 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 5.5% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Robotics Welding Market Size 2024 |
USD 8.49 billion |
| Robotics Welding Market, CAGR |
5.5% |
| Robotics Welding Market Size 2032 |
USD 13.02 billion |
The robotics welding market is characterized by the presence of major global players including Fanuc Corporation, Panasonic Corporation, Yaskawa Electric Corporation, Kuka AG, Daihen Corporation, ABB Ltd., and Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. These companies lead through advanced automation technologies, strong R&D capabilities, and extensive distribution networks. They focus on developing high-precision, AI-integrated welding systems that improve productivity and reduce operational costs. North America emerged as the leading region, accounting for a 36% share in 2024, driven by the rapid adoption of industrial automation in automotive and heavy machinery sectors. This dominance reflects strong manufacturing infrastructure and high investment in smart factory integration.
Market Insights
- The robotics welding market was valued at USD 8.49 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 13.02 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 5.5%.
- Market growth is driven by rising automation in manufacturing, expanding electric vehicle production, and increasing need for precision welding in industrial applications.
- Key trends include AI-powered welding systems, adoption of collaborative robots, and growing demand for laser and hybrid welding technologies.
- The market remains competitive, with global manufacturers focusing on advanced automation, AI integration, and strategic partnerships to enhance efficiency and global reach.
- North America led with a 36% share in 2024, followed by Asia-Pacific with 31% and Europe with 29%; the arc welding segment dominated with a 41% share, supported by widespread use in automotive and machinery industries.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
Arc welding held the largest share of 41% in 2024, driven by its versatility and precision in automotive and heavy machinery manufacturing. It offers consistent weld quality, lower production time, and compatibility with diverse materials. Rising automation in vehicle assembly lines and industrial fabrication boosts adoption. MIG and laser welding are also expanding due to increasing demand for high-speed and accurate joining in electronics and aerospace sectors. Manufacturers are integrating advanced sensors and AI control in arc welding robots to improve efficiency and reduce human intervention.
- For instance, KUKA’s ArcSense tracks fillet and V-welds on plate thicknesses greater than 3 mm for real-time torch correction.
By Payload
The 50–150 kg payload segment dominated with a 47% market share in 2024. This range offers a balance between flexibility and lifting capacity, making it ideal for automotive, metal fabrication, and equipment assembly lines. These robots handle medium to heavy components efficiently while maintaining accuracy. Growing demand for modular welding robots that support varied part sizes is driving adoption. Automation of mid-weight assembly operations, especially in electric vehicle and machinery production, further supports segment leadership across industrial manufacturing sectors.
- For instance, FANUC’s R-1000iA/130F handles 130 kg payload with 2,230 mm reach for compact welding cells.
By End Use
The automotive and transportation segment led the market with a 52% share in 2024. Vehicle manufacturers rely heavily on robotic welding for chassis, body panels, and exhaust systems to achieve uniform welds and high productivity. Increasing electric vehicle production and the shift toward lightweight materials like aluminum strengthen robotic adoption. Metals and machinery industries are following closely as automation helps cut labor costs and improve precision. Integration of collaborative robots in automotive assembly lines enhances safety and production throughput, sustaining segment dominance.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Automation in Manufacturing
The growing shift toward industrial automation is driving widespread adoption of robotic welding systems. Manufacturers are deploying robots to improve productivity, maintain consistent weld quality, and reduce human error in repetitive tasks. The automotive, electronics, and machinery industries are rapidly automating their welding operations to meet high-volume production targets. Rising labor costs and worker safety concerns are further accelerating demand for automated welding technologies, especially in regions such as North America and Asia-Pacific, where large-scale manufacturing facilities are integrating robotics to enhance operational efficiency.
- For instance, Volkswagen ordered 700+ KUKA robots for body-in-white production at its Pamplona plant.
Increasing Demand in Automotive and EV Production
Expanding automotive and electric vehicle manufacturing is a major driver for robotic welding systems. Automakers are adopting welding robots for precision assembly, lightweight material integration, and faster cycle times. The need for reliable and uniform welds in battery packs, vehicle frames, and structural components is promoting automation. As electric mobility expands globally, manufacturers are investing in robotic solutions to streamline complex joining processes and enhance production scalability, resulting in higher efficiency and reduced operational downtime across assembly plants.
- For instance, Tesla reported its Shanghai welding workshop automation rate is close to 100% during 2024 operations.
Advancements in Robotic Sensing and AI Integration
Technological progress in sensors, machine vision, and AI-based control systems is strengthening robotic welding capabilities. Intelligent welding robots can now self-adjust parameters, detect defects, and optimize performance in real time. These advancements reduce rework, minimize material waste, and ensure superior weld quality. Integration of AI-powered analytics also enables predictive maintenance and process monitoring, improving equipment uptime. The convergence of robotics with digital manufacturing and smart factory initiatives is enhancing process automation and shaping the next phase of welding innovation.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Adoption of Collaborative Welding Robots (Cobots)
Collaborative robots are emerging as a transformative trend in robotic welding. These cobots can work safely alongside human operators, offering flexibility and cost savings for small and medium enterprises. The integration of force sensors, intuitive programming, and compact designs makes them ideal for low-volume, high-mix production environments. Growing use of cobots in metal fabrication and custom automotive workshops provides an opportunity for expanding robotic welding adoption beyond large-scale manufacturing, enhancing accessibility and affordability across industries.
- For instance, Universal Robots has sold more than 100,000 cobots worldwide, with many deployed in applications such as welding, machine tending, and material handling.
Shift Toward Laser and Hybrid Welding Technologies
Laser and hybrid welding systems are gaining traction as industries seek faster and more precise welding techniques. Laser welding offers deep penetration, minimal distortion, and cleaner joints, making it suitable for high-end applications in aerospace, automotive, and electronics. Hybrid systems combine laser and arc welding advantages, enabling improved control and reduced heat input. The trend toward advanced materials and lightweight components is accelerating demand for these high-performance welding technologies, presenting new opportunities for robot manufacturers and system integrators.
- For instance, IPG Photonics’ battery module systems weld up to 15 cylindrical cells per second in automated lines.
Expansion in Emerging Manufacturing Hubs
Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are witnessing increased investments in robotic welding infrastructure. Rising industrialization, government incentives for automation, and the establishment of new manufacturing facilities are fueling market expansion. Local companies are partnering with global robot manufacturers to deploy advanced welding solutions in automotive, construction, and metalworking sectors. This regional growth offers significant opportunities for technology providers to strengthen their presence and support local industries transitioning toward smart manufacturing systems.
Key Challenges
High Initial Investment and Integration Costs
The high cost of robotic welding systems and their integration into existing production lines remains a major challenge. Small and medium manufacturers often face budget constraints when adopting these advanced technologies. Installation, programming, and maintenance add to overall project expenses, delaying return on investment. Despite long-term benefits like reduced labor costs and higher efficiency, the upfront capital requirement limits adoption in developing regions, where cost-sensitive industries still rely heavily on manual or semi-automated welding processes.
Skilled Workforce Shortage and Technical Complexity
The growing need for skilled professionals capable of operating and maintaining robotic welding systems poses a significant challenge. Advanced robots require expertise in programming, calibration, and data-driven process control. The shortage of trained technicians often leads to underutilization or operational inefficiencies. Continuous technological evolution adds further complexity, demanding regular workforce training. Bridging the skills gap through vocational programs and partnerships between manufacturers and educational institutions is crucial to ensure successful implementation and sustained productivity in robotic welding operations.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America held a 36% market share in 2024, driven by strong demand from the automotive and heavy machinery sectors. The United States leads regional adoption due to high labor costs and the growing need for precision manufacturing. Leading manufacturers are integrating robotic welding systems to enhance productivity and safety in large-scale production lines. Expanding electric vehicle assembly facilities and investments in smart manufacturing initiatives further support market growth. Technological advancements, government incentives for automation, and the presence of major robotics suppliers continue to strengthen regional competitiveness in industrial automation.
Europe
Europe accounted for a 29% share of the robotics welding market in 2024, supported by advanced automation adoption across automotive and aerospace industries. Germany, France, and Italy dominate regional demand with robust manufacturing infrastructure and high-quality standards. European companies are investing in energy-efficient and precision welding solutions to comply with sustainability goals. The shift toward Industry 4.0 and collaborative robotics in industrial operations enhances process flexibility and worker safety. Increasing demand for lightweight material welding, particularly in electric vehicle and aerospace manufacturing, further drives robotic welding deployment across the region.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific led the global robotics welding market with a 31% share in 2024, reflecting rapid industrialization and large-scale automation adoption. China, Japan, and South Korea remain the primary hubs due to high automotive production and electronics manufacturing. The region benefits from low-cost manufacturing, expanding infrastructure, and strong government support for industrial robotics. Local robot manufacturers are gaining prominence by offering cost-effective and customizable welding systems. Growing electric vehicle production and increased investments in smart factories further enhance regional growth, positioning Asia-Pacific as a key contributor to global welding automation expansion.
Latin America
Latin America captured a 2% share of the robotics welding market in 2024, with Brazil and Mexico leading adoption in automotive and metal fabrication industries. The region is gradually embracing automation to improve efficiency and reduce dependence on manual welding. Foreign investments in automotive component manufacturing and industrial machinery are driving robotic deployment. Despite slower technological adoption compared to other regions, growing awareness of production quality and safety standards supports gradual expansion. Increasing availability of affordable robotic systems and regional training programs is expected to strengthen market penetration in the coming years.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounted for a 2% market share in 2024, primarily driven by industrial diversification and infrastructure development projects. Countries such as the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa are investing in automated welding systems to modernize manufacturing and energy operations. The oil and gas, construction, and metal fabrication sectors are key end users adopting welding robots for improved precision and productivity. Government initiatives promoting industrial automation and partnerships with global technology providers are gradually boosting market presence across this region.
Market Segmentations:
By Type
- Arc welding
- Spot welding
- MIG (Metal Inert Gas)
- TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas)
- Laser welding
- Others
By payload
- 50 kg payload
- 50-150 kg payload
- >150 kg Payload
By End Use
- Automotive & transportation
- Metals & machinery
- Electrical & electronics
- Aerospace & defense
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- U.K.
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- India
- China
- Japan
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The robotics welding market features strong competition among major global players such as Fanuc Corporation, Panasonic Corporation, Yaskawa Electric Corporation, Kuka AG, Daihen Corporation, ABB Ltd., and Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. These companies compete through technological innovation, product diversification, and expansion of automated welding solutions across key industrial sectors. Market leaders focus on enhancing precision, energy efficiency, and system flexibility through AI-based control systems and advanced sensors. Strategic partnerships, acquisitions, and regional expansion help strengthen their supply networks and customer reach. Increasing emphasis on smart factories and Industry 4.0 integration drives companies to invest heavily in R&D for next-generation robotic welding systems. The competitive landscape is further shaped by efforts to reduce equipment costs, improve interoperability, and offer customized automation solutions tailored to automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication applications.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In 2023, ABB At the FABTECH conference, showcased new technologies aimed at simplifying robotic welding for users without extensive programming knowledge. These included a collaborative robot (cobot) arc welding package with an “Easy Teach Device” for lead-through programming.
- In 2023, FANUC showcased its latest automated welding and coating technologies at FABTECH.
- In 2023, KUKA Promoted the new KR CYBERTECH nano ARC HW Edition robot, a budget-friendly and efficient entry-level arc welding robot.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Payload, End-Use and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The robotics welding market will continue expanding due to automation in industrial manufacturing.
- Advancements in AI and machine vision will enhance welding accuracy and consistency.
- Collaborative robots will gain wider adoption across small and medium enterprises.
- Demand from electric vehicle manufacturing will remain a key growth catalyst.
- Integration of IoT and predictive analytics will optimize welding process monitoring.
- Hybrid and laser welding robots will see increased deployment in high-precision sectors.
- Workforce training and robotics education will become critical for sustained adoption.
- Cost reduction in mid-range robots will improve accessibility for emerging markets.
- Sustainability initiatives will drive the use of energy-efficient and eco-friendly welding systems.
- Strategic partnerships between robotics manufacturers and system integrators will accelerate market innovation.




