Market Overview
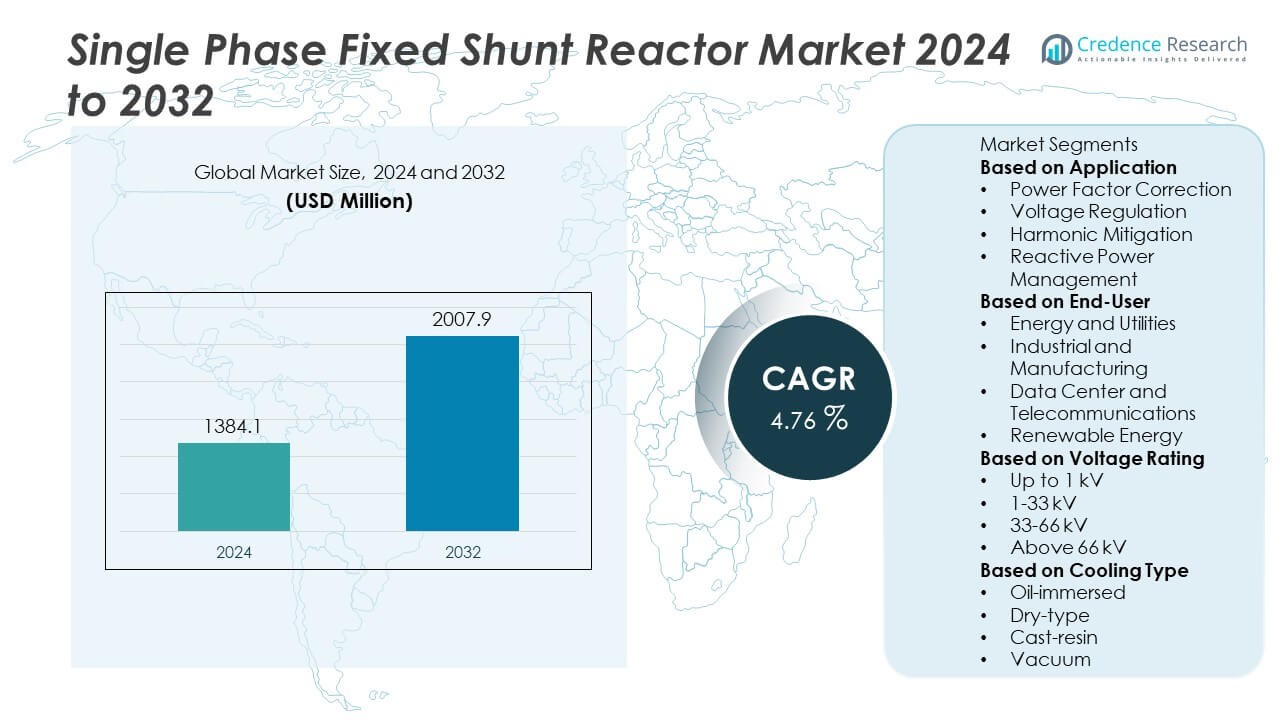
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market was valued at USD 1,384.1 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 2,007.9 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 4.76% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2024 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market Size 2024 |
USD 1,384.1 Million |
| Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market, CAGR |
4.76% |
| Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market Size 2032 |
USD 2,007.9 Million |
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market grows with strong drivers and evolving trends supported by rising electricity demand, renewable energy integration, and grid modernization projects. Utilities adopt these reactors to control voltage fluctuations, improve transmission efficiency, and enhance system stability.
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market demonstrates strong geographical adoption across North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa, with each region contributing through distinct priorities. North America emphasizes grid modernization and transmission upgrades to improve reliability under rising renewable integration. Europe focuses on sustainable energy policies and advanced power infrastructure supported by regulatory compliance. Asia Pacific leads growth with large-scale industrialization, smart grid projects, and investments in high-voltage transmission lines. Latin America and the Middle East & Africa adopt shunt reactors to stabilize networks and expand electrification projects. Key players driving the market include Siemens, ABB, Mitsubishi Electric, and General Electric, who strengthen competitiveness through advanced design innovations, digital monitoring technologies, and expanded service networks. Companies like Eaton and Hitachi also enhance market presence by providing energy-efficient and compact solutions tailored to meet both developed and emerging region demands.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market was valued at USD 1,384.1 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 2,007.9 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 4.76% during the forecast period.
- Rising demand for reliable power transmission and distribution strengthens adoption, as utilities rely on shunt reactors to regulate voltage levels, minimize transmission losses, and stabilize high-voltage networks.
- The market reflects trends such as integration of smart grid technologies, digital monitoring, and IoT-enabled systems that enhance operational efficiency and real-time diagnostics in power infrastructure.
- Competitive dynamics feature global players such as Siemens, ABB, Mitsubishi Electric, and General Electric, who expand portfolios through advanced reactor designs, compact solutions, and stronger service networks to secure global presence.
- Market restraints include high initial capital investments, installation complexity, and growing concerns about maintenance costs, which impact adoption in cost-sensitive regions with limited infrastructure budgets.
- Regional analysis highlights North America focusing on modernization and renewable integration, Europe emphasizing regulatory-driven grid efficiency, Asia Pacific leading with large-scale industrialization and smart grid expansion, while Latin America and the Middle East & Africa gradually adopt reactors for electrification and stability improvements.
- Long-term outlook points to growing opportunities in renewable integration, urbanization-driven infrastructure development, and deployment of energy-efficient solutions, ensuring that Single-Phase fixed shunt reactors remain essential in advancing global transmission and distribution networks.
Market Drivers
Rising Need for Reactive Power Compensation in Transmission Networks
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market grows with increasing demand for reactive power management across high-voltage networks. Utilities adopt these reactors to stabilize voltage fluctuations and improve transmission efficiency. It supports grid operators by reducing power losses and enhancing overall reliability. Rapid urbanization and growing electricity demand accelerate the use of fixed shunt reactors in transmission lines. Large-scale projects for power infrastructure expansion strengthen this trend. Governments emphasize investments in energy-efficient transmission systems, driving continued adoption.
- For instance, ABB deployed over 500 units of shunt reactors rated up to 800 kV in China’s ultra-high-voltage transmission lines, ensuring a reduction of nearly 50 MW of reactive power losses per corridor.
Growing Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market benefits from rising deployment of renewable energy, including solar and wind farms, which create variable loads on power systems. It helps manage voltage imbalances caused by intermittent renewable generation. Grid operators require stable compensation equipment to maintain consistent energy flow. Expanding renewable capacity in both developed and emerging economies supports the role of shunt reactors in stabilizing networks. National energy transition policies encourage deployment in hybrid and green grids. Increased renewable penetration ensures sustained reliance on fixed shunt reactors.
- For instance, Siemens supplied single-phase shunt reactors of 420 kV rating for the German TenneT offshore wind grid connection project, supporting renewable integration that delivers more than 800 MW of wind power to the mainland.
Expansion of Power Infrastructure and Smart Grid Initiatives
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market expands with continuous modernization of grid infrastructure and growing adoption of smart grid technologies. It provides advanced solutions that align with digital monitoring systems and automated control platforms. Governments and utilities invest in projects to strengthen transmission capacity in response to rising electricity demand. Urban development, industrial growth, and rural electrification programs create new opportunities for deployment. The integration of smart substations with shunt reactors ensures higher efficiency and reliability. Strong infrastructure commitments globally anchor long-term market demand.
Rising Investments in High-Voltage and Extra-High-Voltage Projects
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market gains momentum through increasing investments in high-voltage and extra-high-voltage transmission projects. It supports utilities in reducing overvoltage conditions in long-distance power lines. The deployment of extra-high-voltage networks for cross-border electricity trade strengthens the need for stable compensation devices. Industrialization in developing regions drives expansion of transmission corridors requiring shunt reactors. Large interconnection projects between countries and regions further stimulate adoption. Continuous growth in high-capacity grids secures the role of Single-Phase fixed shunt reactors in future energy systems.
Market Trends
Adoption of Advanced Monitoring and Control Systems
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market reflects a strong trend toward integration with advanced monitoring and control technologies. Utilities deploy digital platforms and intelligent sensors to track performance in real time. It improves operational efficiency by detecting faults early and enabling predictive maintenance. Grid operators benefit from better visibility across transmission networks, enhancing reliability. Remote monitoring also reduces manual intervention and downtime. The growing alignment of reactors with digital substations reinforces their role in smart grid ecosystems.
- For instance, General Electric implemented its Digital Substation platform in France with over 250 shunt reactors integrated with online condition monitoring sensors, enabling predictive diagnostics that reduced outage time by 30%.
Growing Deployment in Renewable Energy Grids
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market aligns with the expansion of renewable energy projects, especially solar and wind farms. It stabilizes voltage fluctuations created by variable generation and ensures smoother grid integration. Utilities adopt reactors in hybrid networks where renewable energy contributes a significant share. National energy policies promoting clean power accelerate this adoption. Demand is rising in both advanced and emerging economies where renewable capacity continues to expand. The ability to support flexible and sustainable grids positions reactors as vital assets in modern energy systems.
- For instance, Hitachi Energy supplied 765 kV single-phase shunt reactors for India’s Pugalur–Thrissur HVDC transmission project, supporting renewable energy flow of over 6,000 MW into the national grid.
Shift Toward Compact and Modular Reactor Designs
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market shows a trend toward compact and modular designs that provide flexibility in installation and operation. It addresses space limitations in urban substations and industrial facilities. Manufacturers focus on modular reactors that simplify upgrades and reduce project timelines. Compact designs also lower logistics costs and improve adaptability across different grid environments. Utilities prefer solutions that balance cost efficiency with high performance. This shift highlights the move toward more scalable and versatile compensation technologies.
Integration with Extra-High-Voltage Transmission Projects
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market gains traction with expanding extra-high-voltage (EHV) and ultra-high-voltage (UHV) transmission projects. It plays a critical role in maintaining stability in long-distance power transmission corridors. Cross-border electricity trade and interconnection projects demand reliable shunt reactors to manage reactive power. Utilities implement these systems to reduce energy losses and improve power quality. The expansion of high-capacity transmission networks across Asia, Europe, and the Middle East drives this trend. Strong focus on efficiency and reliability reinforces demand for Single-Phase fixed shunt reactors in global projects.
Market Challenges Analysis
High Capital Costs and Complex Installation Requirements
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market faces challenges due to high capital costs and complex installation processes. Utilities and industries must allocate significant budgets to procure and integrate reactors into power networks. It requires specialized infrastructure, heavy equipment, and skilled professionals, which increases project timelines and expenses. Smaller utilities in developing economies often delay adoption because of budget constraints. Maintenance costs also remain high, particularly in regions with harsh environmental conditions. These financial and technical barriers restrict broader deployment across cost-sensitive markets.
Operational Risks and Limited Skilled Workforce Availability
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market encounters risks related to operational reliability and shortage of skilled workforce. It is vulnerable to insulation breakdown, overheating, and mechanical stresses in high-voltage environments, which affect performance over time. Utilities face challenges in ensuring continuous monitoring and preventive maintenance to reduce failure risks. A shortage of trained engineers and technicians limits the efficiency of operation and troubleshooting. Developing regions struggle with limited technical expertise, slowing down adoption of advanced designs. Growing demand for skilled resources intensifies competition, further straining project execution.
Market Opportunities
Rising Integration of Renewable Energy and Smart Grid Expansion
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market presents strong opportunities through rising integration of renewable energy projects and expansion of smart grids. It stabilizes power networks by managing reactive power flow and ensuring voltage control when renewable sources such as wind and solar create fluctuations. Governments invest heavily in renewable capacity additions, which demand efficient power quality equipment. The increasing deployment of smart grids also opens opportunities for advanced reactor designs with real-time monitoring. Utilities prioritize solutions that support long-distance power transmission with minimal losses. The growth of distributed generation systems creates a long-term need for fixed shunt reactors.
Infrastructure Modernization and Emerging Market Adoption
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market benefits from ongoing infrastructure modernization and industrial growth in emerging economies. It supports power transmission projects linked to urban development, industrial parks, and rural electrification. Governments allocate budgets for upgrading outdated grid infrastructure, creating consistent opportunities for suppliers. Rapid industrialization in Asia, Africa, and Latin America increases demand for stable and reliable electricity supply. Compact and cost-effective reactor designs cater to space-constrained urban areas and developing regions with budget limitations. Global suppliers that offer modular and efficient solutions gain competitive advantage in capturing this expanding demand.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Application
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market divides by application into transmission lines, substations, and renewable energy integration. Transmission lines represent the leading application, as reactors ensure voltage stability and reactive power compensation in long-distance high-voltage lines. It prevents over-voltage conditions and improves overall network reliability, which is essential in inter-regional power transfer. Substations adopt shunt reactors for reactive power control, ensuring stable voltage profiles during fluctuating load conditions. Renewable energy projects also rely on fixed shunt reactors to stabilize voltage swings created by intermittent sources like wind and solar. The application range demonstrates the importance of reactors in ensuring efficiency and operational safety across modern grids.
- For instance, Siemens supplied 765 kV single-phase fixed shunt reactors is incorrect. The primary supplier of the ±800 kV converter technology was Hitachi Energy. Shunt reactors are a separate type of equipment that helps manage reactive power in the grid.
By End-User
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market segments by end-user into utilities, industries, and renewable energy operators. Utilities dominate due to large-scale investments in power transmission and distribution networks. It strengthens their capability to manage growing electricity demand and grid modernization initiatives. Industrial users adopt reactors to maintain stable operations in manufacturing facilities with high power requirements. Renewable energy operators deploy reactors for integrating variable energy generation into national grids without compromising power quality. The diversity of end-users reflects the adaptability of shunt reactors across multiple power system environments.
- For instance, ABB deployed over 300 units of oil-immersed single-phase shunt reactors across utility substations in Brazil, each rated at 500 Mvar, ensuring reliable grid support for both industrial loads and renewable energy integration.
By Voltage Rating
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market categorizes by voltage rating into below 220 kV, 220–500 kV, and above 500 kV. Reactors rated below 220 kV are widely used in distribution systems and localized industrial grids where voltage fluctuations must be controlled at smaller scales. The 220–500 kV range dominates transmission networks, where it manages reactive power and stabilizes inter-regional energy flows. It ensures optimal functioning of high-capacity lines that serve urban and industrial clusters. Reactors above 500 kV find application in ultra-high-voltage transmission systems, supporting bulk power transfer across long distances. The segmentation highlights how varied voltage requirements align with the expansion of global power networks.
Segments:
Based on Application
- Power Factor Correction
- Voltage Regulation
- Harmonic Mitigation
- Reactive Power Management
Based on End-User
- Energy and Utilities
- Industrial and Manufacturing
- Data Center and Telecommunications
- Renewable Energy
Based on Voltage Rating
- Up to 1 kV
- 1-33 kV
- 33-66 kV
- Above 66 kV
Based on Cooling Type
- Oil-immersed
- Dry-type
- Cast-resin
- Vacuum
Based on the Geography:
- North America
- Europe
- UK
- France
- Germany
- Italy
- Spain
- Russia
- Belgium
- Netherlands
- Austria
- Sweden
- Poland
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Thailand
- Indonesia
- Vietnam
- Malaysia
- Philippines
- Taiwan
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Peru
- Chile
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East
- UAE
- KSA
- Israel
- Turkey
- Iran
- Rest of Middle East
- Africa
- Egypt
- Nigeria
- Algeria
- Morocco
- Rest of Africa
Regional Analysis
North America
North America accounts for 28% of the Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market, supported by large-scale investments in grid modernization and renewable energy integration. The United States leads regional demand through ongoing upgrades of transmission infrastructure and expansion of ultra-high-voltage lines. It benefits from federal initiatives that promote the integration of renewable energy, requiring stable grid management solutions provided by shunt reactors. Canada contributes with significant investment in hydroelectric and wind power projects, where reactors support voltage stabilization across long-distance transmission networks. Mexico demonstrates steady adoption in industrial hubs and cross-border energy trade. The presence of leading power utilities and supportive regulatory frameworks reinforces consistent demand for fixed shunt reactors across North America.
Europe
Europe holds 25% of the Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market, driven by its strong focus on renewable energy expansion and grid stability. Germany, France, and the UK lead adoption with large-scale wind and solar projects requiring advanced voltage regulation. It also benefits from cross-border electricity trading under the European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity (ENTSO-E), which demands reliable grid balancing technologies. Eastern European countries adopt shunt reactors as part of modernization programs aimed at reducing transmission losses and enhancing efficiency. The European Union’s stringent energy policies and investments in smart grid development further drive growth. The emphasis on sustainable energy systems ensures that shunt reactors remain integral to Europe’s evolving energy infrastructure.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific dominates the Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market with 32% share, supported by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and expansion of high-capacity power networks. China and India lead the region with large-scale investments in ultra-high-voltage transmission systems that require advanced voltage stability solutions. It benefits from rising electricity demand across urban and industrial clusters, where reactors enhance grid reliability. Japan and South Korea contribute with significant adoption in renewable energy integration, particularly offshore wind and solar projects. Southeast Asian nations, including Vietnam and Indonesia, show increasing demand as they expand electrification and modernize infrastructure. Strong government-backed energy transition programs secure Asia Pacific’s position as the largest and fastest-growing regional market.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for 9% of the Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market, led by Brazil, Mexico, and Chile. Brazil’s hydropower-dominated grid creates strong demand for shunt reactors to manage fluctuating reactive power flows. Mexico continues to invest in strengthening its transmission and distribution networks to support industrial growth and renewable adoption. Chile and Argentina enhance grid reliability through investments in wind and solar projects, where reactors mitigate voltage instability. Regional adoption reflects a balance between modernization efforts and budgetary constraints, with governments promoting infrastructure upgrades. Partnerships with international suppliers and financing institutions strengthen Latin America’s ability to deploy advanced shunt reactors across critical projects.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa hold 6% of the Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market, with adoption driven by grid expansion and renewable diversification strategies. Gulf countries such as Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates deploy reactors to integrate solar and wind energy into their national grids. It also supports large-scale transmission projects designed to improve interconnectivity across the Gulf region. In Africa, South Africa, Nigeria, and Egypt lead adoption, focusing on stabilizing unreliable grids and supporting rural electrification. Governments prioritize investments in compact and cost-effective shunt reactors for industrial and urban development projects. While adoption remains slower compared to other regions, growing energy demand and infrastructure development continue to create long-term opportunities.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Crompton Greaves
- ABB
- Eaton
- Hitachi
- Siemens
- Havells India
- General Electric
- Larsen Toubro
- Schneider Electric
Competitive Analysis
The competitive landscape of the Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market is defined by global leaders such as Siemens, ABB, Mitsubishi Electric, General Electric, Eaton, Schneider Electric, Hyundai Electric Energy Systems, Crompton Greaves, Hitachi, and Larsen & Toubro, who compete through innovation, global reach, and industry expertise. Siemens and ABB dominate with advanced high-voltage reactor solutions integrated with digital monitoring and automation, ensuring grid stability and efficiency across large-scale networks. Mitsubishi Electric and Hitachi focus on delivering compact and energy-efficient shunt reactors tailored for renewable energy integration and smart grid projects. General Electric and Eaton emphasize modular designs and service flexibility to meet the evolving needs of utilities and industrial end-users. Schneider Electric leverages its expertise in power management by combining reactors with IoT-enabled monitoring systems for real-time performance optimization. Hyundai Electric Energy Systems and Crompton Greaves strengthen competitiveness by offering cost-efficient solutions for emerging markets with growing electrification needs. Larsen & Toubro expands its position by supplying robust equipment for large infrastructure and power transmission projects in developing regions. Across the market, these players prioritize advanced engineering, strategic collaborations, and global service networks, enabling them to meet rising demand for reliable power transmission and sustainable grid operations.
Recent Developments
- In February 2025, Mitsubishi Electric partnered with a utility provider to enhance grid stability via new reactor installations.
- In November 2024, ABB launched a new range of air‑core single‑phase fixed shunt reactors engineered for power transmission networks.
- In November 2024, Siemens completed deployment of a large‑scale single‑phase fixed shunt reactor for a major industrial client.
- In October 2024, Schneider Electric expanded its product portfolio to include advanced iron‑core fixed shunt reactors.
Market Concentration & Characteristics
The Single-Phase Fixed Shunt Reactor Market reflects a moderately consolidated structure dominated by global players with strong technological expertise, supported by regional manufacturers serving localized demand. Leading companies such as ABB, Siemens, GE, Mitsubishi Electric, and Schneider Electric hold significant positions through their wide portfolios and proven capabilities in delivering efficient, grid-stabilizing solutions. It remains competitive with regional participants like Crompton Greaves and Havells India who provide cost-effective products tailored for emerging markets. The market emphasizes reliability, high-voltage efficiency, and operational durability, with utilities prioritizing reactors that reduce losses and improve grid performance. It adapts to varied needs across industrial, commercial, and power transmission sectors, reflecting flexibility in deployment across voltage ratings and applications. Growing emphasis on renewable integration and grid modernization drives innovation in compact and energy-efficient reactor designs. The balance between large multinational corporations driving technological advancements and regional firms catering to budget-sensitive projects defines the market’s characteristics, reinforcing its essential role in modern power systems.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Application, End-User, Voltage Rating, Cooling Type and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Market growth will align with rising electricity demand across industrial, residential, and commercial sectors.
- Renewable energy integration will strengthen adoption of shunt reactors for grid stability.
- Smart grid expansion will increase demand for compact and digitally monitored reactor systems.
- Manufacturers will focus on energy-efficient and low-loss reactor designs.
- Emerging economies will drive large-scale adoption through electrification and infrastructure projects.
- Utilities will invest in reactors to reduce transmission losses and enhance power quality.
- Continuous R&D will improve insulation materials and thermal management systems.
- Strategic partnerships between global leaders and regional suppliers will expand technology access.
- Growing urbanization will accelerate deployment in distribution networks and metro projects.
- Cybersecure digital monitoring solutions will become standard in advanced shunt reactor systems.




