Market Overview
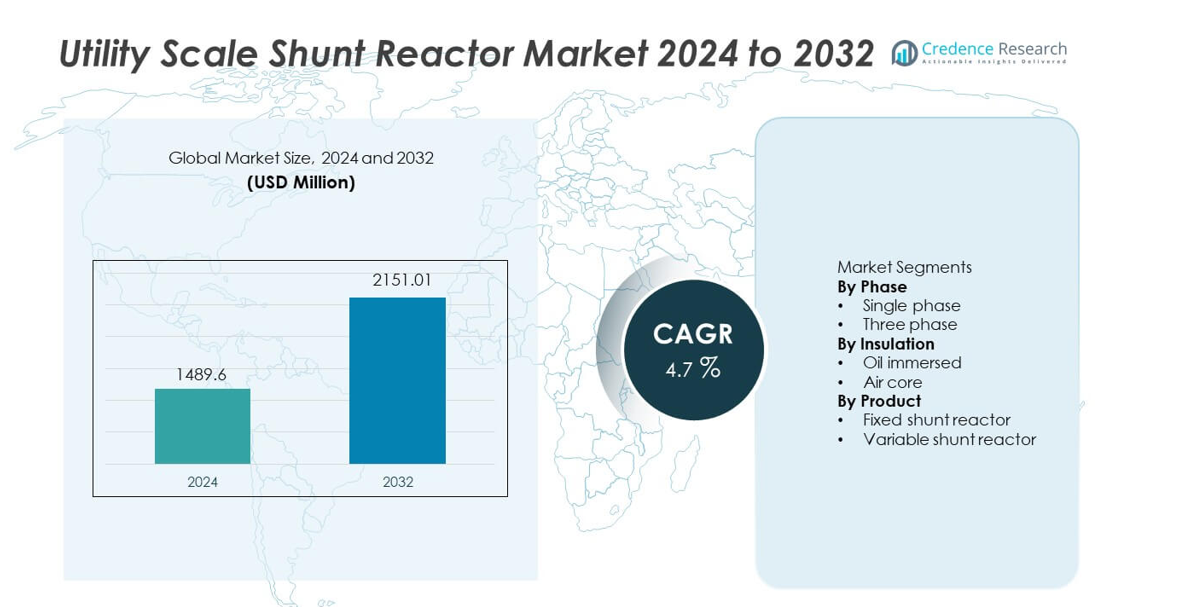
The Utility Scale Shunt Reactor market was valued at USD 1,489.6 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 2,151.01 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 4.7% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Utility Scale Shunt Reactor Market Size 2024 |
USD 1,489.6 million |
| Utility Scale Shunt Reactor Market, CAGR |
4.7% |
| Utility Scale Shunt Reactor Market Size 2032 |
USD 2,151.01 million |
The Utility Scale Shunt Reactor market features strong participation from leading players such as CG Power & Industrial Solutions, Fuji Electric, GE, Hitachi Energy, Hyosung Heavy Industries, Nissin Electric, SGB SMIT, HICO America, GETRA, and GBE. These companies compete through high-voltage engineering expertise, reliable reactor designs, and strong utility partnerships. Asia Pacific leads the market with an exact share of 34.8%, driven by rapid expansion of high-voltage and ultra-high-voltage transmission networks and large renewable evacuation projects. North America follows with a 27.3% share, supported by grid modernization and long-distance transmission upgrades. Europe holds a 23.9% share, supported by offshore wind integration, cross-border interconnections, and strict grid stability requirements. Competitive intensity remains focused on performance reliability, voltage control capability, and large-scale project execution.
Market Insights
- The Utility Scale Shunt Reactor market was valued at USD 1,489.6 million in 2024 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.7% during the forecast period.
- Expansion of high-voltage transmission networks, renewable energy integration, and increasing focus on grid voltage stability act as key drivers for the Utility Scale Shunt Reactor market.
- Fixed shunt reactors dominate the product segment with a market share of 62.7%, supported by lower complexity, cost efficiency, and suitability for continuous reactive power compensation.
- Competitive dynamics remain strong, with major players focusing on high-capacity reactor designs, advanced insulation systems, and long-term reliability, while regional players compete on cost and localized execution.
- Asia Pacific leads regional demand with a 34.8% market share, followed by North America at 27.3% and Europe at 23.9%, driven by transmission expansion, renewable integration, and grid modernization programs.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Phase
The Utility Scale Shunt Reactor market, by phase, includes single phase and three phase configurations, with three phase shunt reactors dominating at a market share of 71.8%. Utilities prefer three phase systems due to integrated design, balanced reactive power compensation, and reduced footprint at substations. These reactors support high-voltage transmission networks and long-distance power corridors more efficiently. Growing expansion of extra-high-voltage and ultra-high-voltage transmission lines strengthens adoption. Single phase reactors remain relevant for specific grid configurations and modular installations, but system complexity and higher installation requirements limit broader use compared to three phase solutions.
- For instance, Hitachi Energy supplies three phase shunt reactors rated up to 765 kV with reactive power capacity reaching 330 MVAr for large transmission networks.
By Insulation
Based on insulation type, the market segments into oil immersed and air core reactors, with oil immersed reactors leading with a market share of 66.4%. Utilities favor oil immersed designs due to superior thermal performance, higher reactive power absorption, and long operational life. These reactors perform reliably in outdoor substations and harsh environmental conditions. Expansion of high-capacity transmission infrastructure further supports demand. Air core reactors gain adoption in applications requiring lower losses and reduced maintenance, but higher space requirements and limited high-voltage suitability restrict widespread deployment at utility scale.
- For instance, GE Vernova manufactures oil immersed shunt reactors with continuous operating temperatures up to 95 °C and reactive ratings above 200 MVAr for utility substations.
By Product
By product type, the market includes fixed shunt reactors and variable shunt reactors, with fixed shunt reactors holding a dominant market share of 62.7%. Utilities deploy fixed reactors for continuous reactive power compensation on long transmission lines and lightly loaded networks. Lower complexity, cost efficiency, and proven reliability support widespread use. Variable shunt reactors gain traction in grids with fluctuating load conditions and renewable energy integration. However, higher capital costs and control complexity limit faster adoption, keeping fixed shunt reactors as the primary choice for utility-scale applications.
Key Growth Drivers
Expansion of High-Voltage Transmission Infrastructure
Rapid expansion of high-voltage and ultra-high-voltage transmission networks strongly drives demand for utility scale shunt reactors. Utilities deploy shunt reactors to control voltage rise on long-distance and lightly loaded transmission lines. Growing interregional power transfer and cross-border grid projects increase installation requirements. Grid modernization programs focus on improving voltage stability and reducing transmission losses. Rising electricity demand from urbanization and industrial growth further supports network expansion. Utility scale shunt reactors remain critical assets for maintaining stable voltage profiles across large transmission systems.
- For instance, Siemens Energy has deployed shunt reactors for 400 kV and 500 kV lines, designed to stabilize transmission routes extending beyond 300 km in national grid projects.
Rising Integration of Renewable Energy Generation
Large-scale integration of wind and solar power increases reactive power imbalance across utility grids. Variable renewable generation creates voltage fluctuations, especially in remote transmission corridors. Utility scale shunt reactors absorb excess reactive power and stabilize grid voltage. Utilities install reactors near renewable evacuation points to meet grid code requirements. Expansion of offshore wind farms and large solar parks accelerates adoption. Renewable energy targets and decarbonization policies further reinforce demand. Grid operators increasingly rely on shunt reactors to maintain reliability under fluctuating generation conditions.
- For instance, ABB supports offshore and onshore wind integration with shunt reactors designed for continuous operation under fluctuating loads, handling reactive absorption above 200 MVAr at coastal grid substations.
Growing Focus on Grid Stability and Power Quality
Power quality and grid stability have become priorities for utilities worldwide. Voltage rise during low-load periods threatens equipment safety and operational reliability. Utility scale shunt reactors provide continuous and cost-effective reactive power compensation. Utilities deploy these systems to protect transformers and transmission assets. Aging grid infrastructure replacement also supports new installations. Investments in grid monitoring and automation strengthen the role of shunt reactors. Stability-driven upgrades continue to support long-term market growth.
Key Trends and Opportunities
Deployment in Ultra-High-Voltage and Long-Distance Transmission Projects
Utilities increasingly invest in ultra-high-voltage transmission corridors to move power efficiently over long distances. These projects require high-capacity shunt reactors for effective voltage control. Expansion of UHV networks in Asia and other regions creates strong opportunities. Manufacturers focus on designing reactors with higher voltage ratings and improved thermal performance. Long-term transmission planning supports sustained demand. This trend creates opportunities for suppliers with advanced high-voltage engineering capabilities.
- For instance, TBEA Co., Ltd. has supplied shunt reactors for 1,100 kV UHV AC transmission projects, with single-unit reactive power ratings reaching 360 MVAr and oil temperature rise limited to 55 °C under continuous operation.
Technological Advancements in Reactor Design and Monitoring
Manufacturers adopt improved insulation systems, advanced materials, and enhanced cooling designs. These innovations increase efficiency and extend operational life. Integration of monitoring sensors supports condition-based maintenance. Utilities benefit from reduced downtime and lower operating risks. Demand grows for reactors with lower losses and higher reliability. Technology-driven differentiation creates opportunities for premium product offerings. Continuous innovation strengthens competitive positioning.
- For instance, GE Vernova integrates online monitoring systems that track dissolved gas levels and load current continuously, enabling utilities to detect insulation degradation years before scheduled maintenance intervals.
Key Challenges
High Capital Investment and Long Project Development Cycles
Utility scale shunt reactors require significant upfront capital investment. Large transmission projects involve long planning and approval timelines. Budget constraints can delay procurement decisions by utilities. Installation schedules often depend on broader grid expansion programs. Long equipment lifecycles reduce replacement frequency. These factors slow short-term market turnover. Manufacturers face pressure to balance cost control with performance and reliability.
Complex Engineering and Site-Specific Integration Requirements
Deployment of utility scale shunt reactors requires detailed grid studies and customized design. Incorrect sizing affects voltage regulation performance. Installation demands skilled engineering and precise coordination. Space constraints and environmental conditions add complexity. Utilities rely on specialized vendors for system integration and commissioning. These technical challenges increase project risk and execution time. Complexity remains a barrier to rapid deployment.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds a market share of 27.3% in the Utility Scale Shunt Reactor market. Demand is driven by grid modernization programs and expansion of long-distance transmission corridors in the United States and Canada. Utilities deploy shunt reactors to manage voltage rise on lightly loaded high-voltage lines. Rising integration of wind and solar power increases reactive power compensation needs. Replacement of aging transmission infrastructure further supports installations. Regulatory focus on grid reliability, resilience, and power quality strengthens adoption. Continued investment in cross-state transmission projects sustains stable regional growth.
Europe
Europe accounts for 23.9% of the global Utility Scale Shunt Reactor market share. Strong renewable energy penetration across Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Nordic countries drives reactor demand. Expansion of offshore wind farms and cross-border interconnections increases voltage regulation requirements. Utilities invest in shunt reactors to maintain grid stability and comply with strict grid codes. Aging transmission asset replacement also supports demand. Energy transition goals and power quality regulations influence procurement decisions. Focus on resilient and interconnected grids supports steady market expansion across the region.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific leads the market with a share of 34.8%. Rapid expansion of high-voltage and ultra-high-voltage transmission networks across China, India, Japan, and Southeast Asia drives strong demand. Large-scale renewable energy evacuation projects increase shunt reactor installations. Governments invest heavily in long-distance power transmission to meet rising electricity consumption. Grid stability challenges in fast-growing networks further support adoption. Industrial growth and urbanization accelerate infrastructure development. Strong utility spending positions Asia Pacific as the dominant regional market.
Latin America
Latin America holds a market share of 8.2% in the Utility Scale Shunt Reactor market. Transmission infrastructure expansion in Brazil, Chile, and Mexico supports steady demand. Renewable energy projects, especially wind and solar, increase voltage control requirements. Utilities deploy shunt reactors to improve grid stability across long transmission routes. Power loss reduction initiatives also contribute to adoption. Budget constraints limit rapid deployment, but ongoing grid upgrades support moderate growth. Focus on improving transmission efficiency strengthens long-term regional demand.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for 5.8% of the global market share. Growth is driven by expansion of high-voltage transmission networks in Gulf countries. Large renewable energy projects and interconnection initiatives increase the need for voltage regulation solutions. Harsh climatic conditions require reliable grid stability equipment. In Africa, gradual electrification and transmission development support adoption. Investments remain concentrated in major infrastructure projects. Long-term power sector development sustains steady regional market progress.
Market Segmentations:
By Phase
By Insulation
By Product
- Fixed shunt reactor
- Variable shunt reactor
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
Competitive landscape analysis highlights a competitive and technology-focused market led by CG Power & Industrial Solutions, Fuji Electric, GE, Hitachi Energy, Hyosung Heavy Industries, Nissin Electric, SGB SMIT, HICO America, GETRA, and GBE. These players compete on reactor reliability, voltage handling capability, and compliance with utility grid standards. Leading manufacturers focus on high-capacity and three-phase shunt reactors to support expanding transmission networks. Investments in advanced insulation systems, thermal management, and condition monitoring strengthen product performance. Strong relationships with utilities and EPC contractors support large-scale project awards. Global players leverage wide manufacturing footprints and service networks, while regional suppliers compete through cost efficiency and localized engineering support. Participation in grid modernization and renewable energy integration projects remains a key strategy. Continuous innovation, project execution capability, and adherence to grid codes define competitive positioning in the Utility Scale Shunt Reactor market.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Hitachi Energy
- SGB SMIT
- CG Power & Industrial Solutions
- Hyosung Heavy Industries
- Nissin Electric
- GE
- Fuji Electric
- HICO America
- GETRA
- GBE
Recent Developments
- In October 2024, Hitachi Energy’s 500 kV variable shunt reactor was manufactured (or “scaled up for application”) to support the development of Uzbekistan’s Dzhankeldy 500 MW wind farm, ensuring grid stability and voltage regulation.
- In August 2024, Hitachi Energy received a record order from Svenska Kraftnät, Sweden’s transmission system operator, to strengthen Sweden’s power grid.
- In February 2024, the Grid Solutions business of General electric secured major contracts from the Power Grid Corporation of India (PGCIL) for manufacturing and supplying 765 kV Shunt Reactors.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Phase, Insulation, Product and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Expansion of high-voltage transmission networks will sustain market demand.
- Renewable energy integration will increase reactive power compensation needs.
- Utilities will invest in voltage stability and grid reliability solutions.
- Ultra-high-voltage transmission projects will drive high-capacity reactor adoption.
- Fixed shunt reactors will remain the preferred choice for continuous compensation.
- Smart monitoring features will gain importance in utility applications.
- Asia Pacific will continue to lead market growth.
- Grid modernization programs will support replacement demand.
- Engineering customization will remain critical for project success.
- Competition will intensify through technology, cost efficiency, and service quality.




