Market Overview
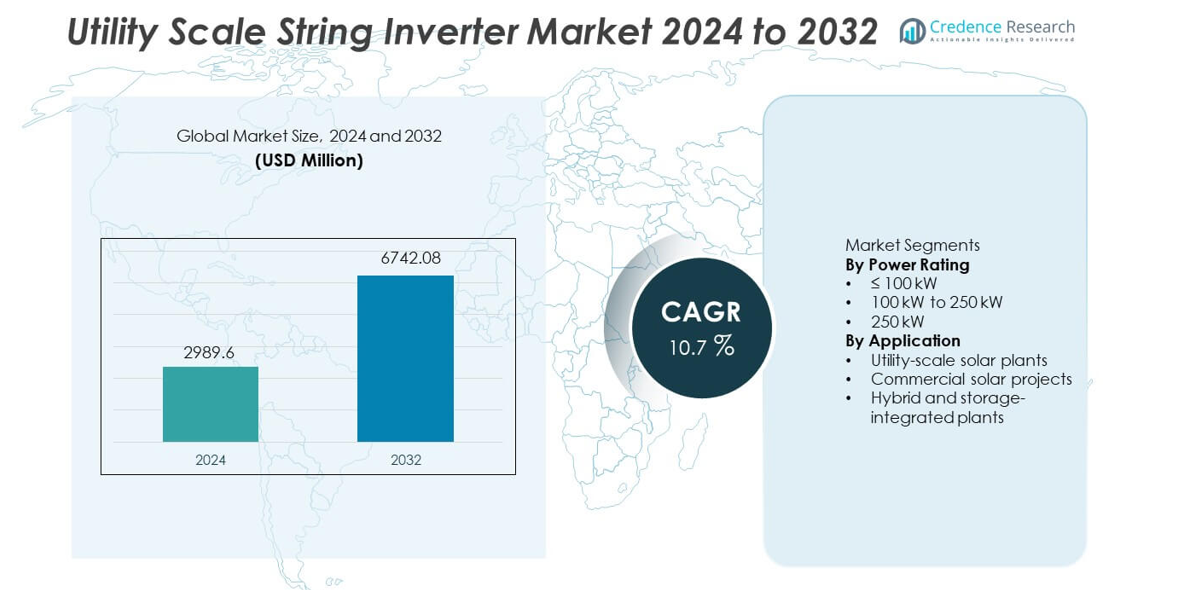
The Utility Scale String Inverter market was valued at USD 2,989.6 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 6,742.08 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 10.7% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Utility Scale String Inverter Market Size 2024 |
USD 2,989.6 million |
| Utility Scale String Inverter Market, CAGR |
10.7% |
| Utility Scale String Inverter Market Size 2032 |
USD 6,742.08 million |
The Utility Scale String Inverter market includes leading players such as Huawei Technologies, Sungrow Power Supply, SMA Solar Technology, FIMER, Ingeteam, Power Electronics, TMEIC, Sineng Electric, Growatt New Energy, and Delta Electronics. These companies compete through high-power inverter designs, advanced grid support functions, and strong EPC partnerships. Asia Pacific leads the market with an exact share of 35.9%, driven by large-scale solar deployments in China, India, and Australia. North America follows with a 27.6% share, supported by utility-scale solar expansion and replacement of older inverter systems. Europe holds a 24.3% share, driven by decarbonization policies and growing hybrid solar and storage projects. Competitive focus remains on efficiency, scalability, and long-term reliability for large solar plants.
Market Insights
- The Utility Scale String Inverter market was valued at USD 2,989.6 million in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.7% during the forecast period.
- Market growth is driven by rapid expansion of utility-scale solar projects, declining inverter costs, and strong government support for renewable energy deployment.
- The 100 kW to 250 kW power rating segment leads with a market share of 46.8%, while utility-scale solar plants dominate application demand with a 58.9% share due to large project installations.
- Competitive dynamics remain strong, with leading players focusing on high-power string inverters, advanced grid support features, digital monitoring, and long-term service capabilities, while cost efficiency drives competition in emerging markets.
- Asia Pacific leads regional demand with a 35.9% market share, followed by North America at 27.6% and Europe at 24.3%, supported by large solar capacity additions, grid modernization, and hybrid project development.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Power Rating
The Utility Scale String Inverter market, by power rating, includes ≤100 kW, 100 kW to 250 kW, and >250 kW categories, with the 100 kW to 250 kW segment leading with a market share of 46.8%. This segment gains strong adoption due to its optimal balance between power density, efficiency, and system flexibility for large solar installations. Utility developers prefer this range for modular plant design, easier maintenance, and reduced downtime compared to central inverters. Improved inverter efficiency, higher DC-to-AC ratios, and better fault tolerance further support adoption. Growing deployment of large solar parks and rising focus on reducing levelized cost of electricity continue to drive dominance of this power range.
- For instance, Sungrow deployed its multi-MPPT inverter featuring a high-capacity DC input, supporting significant DC loading and faster fault recovery in large solar parks.
By Application
By application, the market segments into utility-scale solar plants, commercial solar projects, and hybrid and storage-integrated plants, with utility-scale solar plants accounting for 58.9% market share. Large solar farms increasingly adopt string inverters due to higher system availability, simplified operation, and improved performance under partial shading. Grid support functions such as reactive power control and fault ride-through enhance suitability for utility applications. Rapid expansion of utility-scale solar capacity, supportive renewable energy policies, and declining inverter costs drive strong demand. Hybrid and storage-integrated plants show rising adoption, but utility-scale solar installations remain the primary growth engine.
- For instance, Huawei installed its SUN2000-215K string inverters in large solar farms, offering high maximum efficiency and supporting multiple MPPT channels to manage uneven terrain. These capabilities improve energy yield and operational reliability in large-scale installations.
Key Growth Drivers
Rapid Expansion of Utility-Scale Solar Installations
Rapid growth of utility-scale solar projects strongly drives demand for string inverters. Governments and utilities continue to invest in large solar parks to meet renewable energy targets. String inverters support modular plant design, higher availability, and easier maintenance compared to central inverters. Developers prefer these systems to reduce downtime and improve yield across large installations. Falling solar module costs and supportive policy frameworks further accelerate project deployment. Expansion of solar capacity across emerging and developed regions sustains long-term growth for utility scale string inverters.
- For instance, Sungrow supplied string inverters for a 2,200 MW solar complex in China, where each inverter supports 12 MPPT channels and a maximum DC input voltage of 1,500 V. This configuration improved layout flexibility and reduced maintenance downtime across the site.
Improved Efficiency and Grid Support Capabilities
Advancements in inverter technology significantly enhance system efficiency and grid compatibility. Modern string inverters offer higher conversion efficiency, advanced monitoring, and improved fault detection. Grid support functions such as reactive power control and voltage regulation improve compliance with utility grid codes. These features increase adoption in large solar plants connected to weak or variable grids. Utilities favor inverters that support grid stability while maximizing output. Continuous innovation in power electronics remains a strong growth driver.
- For instance, SMA Solar deployed its Sunny Highpower PEAK3 string inverter with a nominal power rating of 150 kW, a maximum efficiency of 98.8, and integrated dynamic reactive power control.
Lower Installation and Maintenance Costs
String inverters reduce overall project costs through simplified installation and modular replacement. Smaller unit sizes lower transport and handling complexity. Maintenance teams can replace individual inverters without shutting down entire plants. This flexibility reduces operational risk and improves system uptime. Developers benefit from lower lifecycle costs and improved return on investment. Cost efficiency remains a key driver supporting wider adoption at utility scale.
Key Trends and Opportunities
Rising Adoption of High-Power String Inverters
The market shows a strong shift toward higher power string inverters above 100 kW. Manufacturers develop models with higher power density and advanced cooling. These systems reduce inverter count while maintaining modular benefits. Utilities adopt high-power units to optimize space and cabling costs. This trend creates opportunities for suppliers offering scalable and high-capacity solutions. Demand for high-power string inverters continues to rise in large solar parks.
- For instance, Sineng Electric developed a 275 kW string inverter supporting a 1,500 V DC system, 12 MPPT inputs, and an operating temperature range up to 60 °C.
Growth of Hybrid and Storage-Integrated Solar Plants
Integration of energy storage with solar plants creates new opportunities. String inverters support flexible system architectures for hybrid projects. Utilities deploy these systems to manage intermittency and improve grid reliability. Growth in battery storage adoption strengthens demand for compatible inverter solutions. Hybrid project development expands market scope beyond conventional solar plants. This trend supports long-term diversification opportunities.
- For instance, Ingeteam deployed its INGECON SUN STORAGE inverter platform supporting battery systems up to 1,500 V DC and a bidirectional power flow rating of 100 kW per unit.
Key Challenges
Grid Compliance and Interconnection Complexity
Utility-scale projects face strict grid code requirements. Inverters must meet evolving standards for voltage, frequency, and fault response. Compliance increases design complexity and testing costs. Delays in certification can slow project timelines. Developers require reliable solutions that meet local grid regulations. Managing diverse grid requirements remains a key challenge for manufacturers.
Harsh Operating Conditions and Reliability Concerns
Utility-scale solar plants operate in extreme environmental conditions. High temperatures, dust, and humidity impact inverter performance. Ensuring long-term reliability under these conditions increases engineering requirements. Maintenance access in remote locations adds complexity. Failures can impact plant output and revenue. Manufacturers must balance cost, durability, and performance to address reliability challenges.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds a market share of 27.6% in the Utility Scale String Inverter market. Growth is driven by large utility-scale solar deployments across the United States and Canada. Developers increasingly prefer string inverters for higher system availability and simplified maintenance. Replacement of aging inverter systems in early solar plants also supports demand. Grid modernization and interconnection standards encourage adoption of advanced inverter technologies with grid support features. Rising investments in solar-plus-storage projects further strengthen demand. Strong project pipelines and stable policy support sustain steady regional market expansion.
Europe
Europe accounts for 24.3% of the global Utility Scale String Inverter market share. Strong renewable energy targets and decarbonization policies drive solar capacity additions across Germany, Spain, France, and Italy. Utilities adopt string inverters to improve energy yield and reduce downtime in large solar parks. Grid flexibility requirements and strict compliance standards favor advanced inverter solutions. Growth in hybrid solar and storage projects also supports demand. Replacement of central inverters in older plants contributes to steady market growth across the region.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific leads the market with a share of 35.9%. Rapid expansion of utility-scale solar capacity across China, India, Japan, and Australia drives strong inverter demand. Governments support large solar parks through national renewable programs. Developers favor string inverters for modular design and faster commissioning. Cost competitiveness and local manufacturing strengthen adoption. Grid expansion in emerging economies further increases installations. High solar project pipelines position Asia Pacific as the dominant and fastest-growing regional market.
Latin America
Latin America holds a market share of 7.4% in the Utility Scale String Inverter market. Growth is supported by rising solar investments in Brazil, Chile, and Mexico. Utilities deploy string inverters to improve performance in large-scale projects located in remote regions. Favorable solar irradiation and renewable auctions encourage project development. Budget sensitivity drives preference for cost-efficient and reliable inverter solutions. Gradual grid upgrades and hybrid project adoption support moderate but consistent regional growth.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for 4.8% of the global market share. Large utility-scale solar projects in the Gulf countries drive demand for string inverters. Harsh climatic conditions favor modular systems with easier maintenance. Government-led renewable initiatives support new installations. In Africa, solar development remains gradual but expanding due to electrification needs. Long-term infrastructure investments and declining solar costs support steady regional market progress.
Market Segmentations:
By Power Rating
- ≤ 100 kW
- 100 kW to 250 kW
- 250 kW
By Application
- Utility-scale solar plants
- Commercial solar projects
- Hybrid and storage-integrated plants
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
Competitive landscape analysis highlights a highly competitive market led by Huawei Technologies, Sungrow Power Supply, SMA Solar Technology, FIMER, Ingeteam, Power Electronics, TMEIC, Sineng Electric, Growatt New Energy, and Delta Electronics. Competition centers on efficiency, reliability, and grid compliance for large solar installations. Leading players invest in high-power string inverters, advanced cooling, and digital monitoring to improve uptime and reduce operating costs. Strong grid support features, including voltage regulation and fault ride-through, strengthen utility acceptance. Manufacturers expand global service networks to support large project portfolios and long-term maintenance contracts. Cost optimization through localized manufacturing and supply chain integration enhances competitiveness, especially in price-sensitive regions. Strategic partnerships with EPC firms and utilities support large-scale deployments. Continuous innovation in power density, cybersecurity, and storage integration defines competitive positioning in the Utility Scale String Inverter market.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In September 2025, SMA Solar Technology AG announced U.S. production plans. The plan covers PEAK3 string inverters for large-scale PV systems.
- In April 2025, FIMER S.p.A. (under new ownership by McLaren Applied) officially announced its participation in Intersolar Europe 2025 to showcase its next-generation energy portfolio.
- In June 2024, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. did showcase the SUN2000-330KTL series as part of its utility PV lineup during the SNEC PV Power Expo in Shanghai
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Power Rating, Application and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Utility-scale solar capacity expansion will sustain strong inverter demand.
- High-power string inverters will gain wider adoption in large solar parks.
- Hybrid solar and storage projects will increase inverter complexity needs.
- Grid support and compliance features will shape product development.
- Modular designs will remain preferred for reliability and uptime.
- Cost optimization will influence procurement decisions by developers.
- Asia Pacific will continue to lead new installations.
- Digital monitoring and analytics will become standard features.
- Harsh climate performance will drive design improvements.
- Competition will intensify through innovation, efficiency, and service quality.




