Market Overview
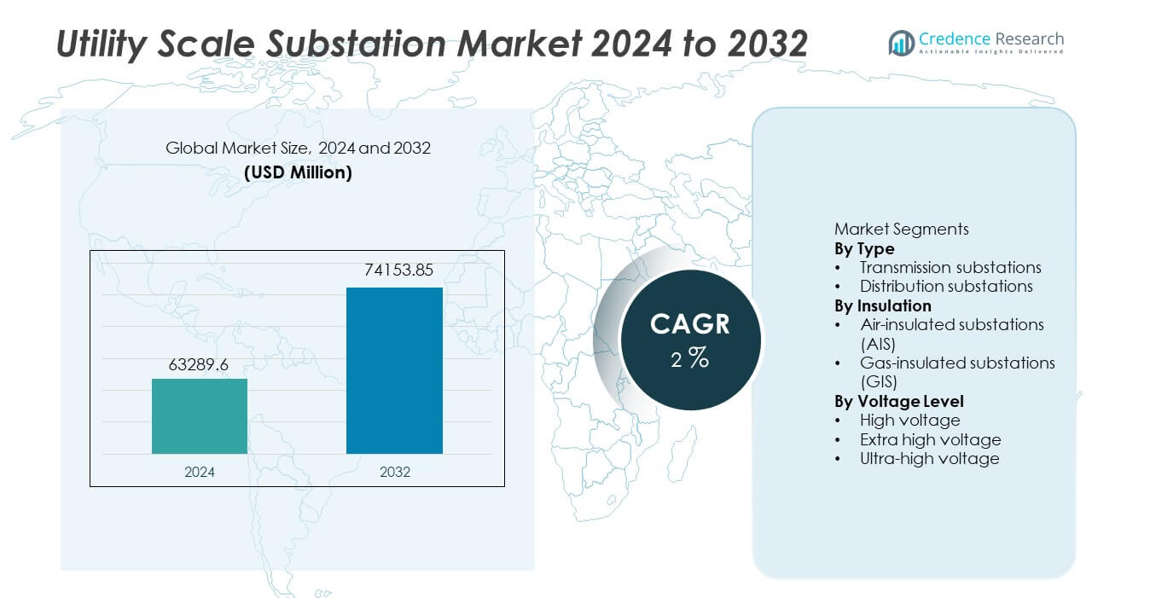
The Utility Scale Substation market was valued at USD 63,289.6 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 74,153.85 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 2% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Utility Scale Substation Market Size 2024 |
USD 63,289.6 million |
| Utility Scale Substation Market , CAGR |
2% |
| Utility Scale Substation Market Size 2032 |
USD 74,153.85 million |
The Utility Scale Substation market features strong participation from Siemens Energy, ABB Ltd., Schneider Electric, General Electric, Hitachi Energy, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Eaton Corporation, Larsen & Toubro, Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions, and Hyundai Electric & Energy Systems. These players compete through turnkey EPC capabilities, high-voltage engineering expertise, and advanced digital substation solutions. Asia Pacific leads the market with an exact share of 37.8%, supported by rapid transmission expansion, urbanization, and large renewable integration projects in China and India. North America follows with a 26.1% market share, driven by grid modernization, replacement of aging substations, and reliability investments. Europe holds a 24.4% share, supported by energy transition goals, cross-border interconnections, and adoption of gas-insulated substations. Competitive strength remains centered on reliability, automation, and large-scale project execution.
Market Insights
- The Utility Scale Substation market was valued at USD 63,289.6 million in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 2% through the forecast period.
- Market growth is driven by transmission network expansion, renewable energy integration, urban electrification, and replacement of aging substation infrastructure across utility grids.
- Gas-insulated substations represent a segment share of 54.2% due to compact design, lower land requirements, and suitability for urban and high-density installations, while transmission substations dominate by type with a 61.7% share.
- Competitive activity remains strong, with global players focusing on digital substations, automation systems, and high-voltage reliability, while regional EPC firms compete through cost efficiency and localized execution.
- Asia Pacific leads the market with a 37.8% regional share, followed by North America at 26.1% and Europe at 24.4%, supported by grid modernization, renewable evacuation projects, and cross-border transmission development.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
The Utility Scale Substation market, by type, includes transmission substations and distribution substations, with transmission substations leading with a market share of 57.8%. Transmission substations play a critical role in stepping up or stepping down voltage for long-distance power transfer across regions. Utilities prioritize these substations to support grid expansion, interregional connectivity, and integration of large renewable energy projects. Rising electricity demand, cross-border power trading, and replacement of aging transmission infrastructure further drive demand. Distribution substations remain essential for local power delivery, but higher investment intensity and strategic importance position transmission substations as the dominant sub-segment.
- For instance, Siemens Energy deployed a 765 kV transmission substation in India supporting power transfer above 6,000 MW across regional grids.
By Insulation
Based on insulation, the market is segmented into air-insulated substations (AIS) and gas-insulated substations (GIS), with AIS accounting for a dominant share of 61.3%. Utilities widely deploy AIS due to lower capital costs, simpler design, and ease of maintenance in areas with sufficient land availability. AIS solutions remain preferred for large outdoor substations in rural and semi-urban regions. However, GIS adoption continues to rise in space-constrained urban environments. Ongoing grid expansion in developing regions and cost-sensitive projects continues to support the dominance of air-insulated substations.
- For instance, Hitachi Energy commissioned an air-insulated substation rated at 400 kV with short-circuit capacity exceeding 63 kA for a national grid expansion project. Gas-insulated substations gain traction in dense urban zones, but air-insulated systems remain widely adopted.
By Voltage Level
By voltage level, the market includes high voltage, extra high voltage, and ultra-high voltage substations, with extra high voltage substations holding the largest share at 48.6%. These substations support bulk power transmission across long distances with reduced losses. Utilities deploy extra high voltage infrastructure to connect large generation sources, including thermal, hydro, and renewable plants, to load centers. Growth in cross-regional transmission corridors and grid reinforcement projects strengthens demand. High voltage substations serve regional networks, while ultra-high voltage systems grow steadily with large-scale national grid projects.
Key Growth Drivers
Grid Modernization and Replacement of Aging Infrastructure
Utilities worldwide invest heavily in modernizing aging substation infrastructure. Many existing substations operate beyond designed lifespans and face reliability risks. Replacement and refurbishment projects drive sustained demand for utility scale substations. Modern substations improve operational efficiency, reduce outage risks, and support advanced grid control. Governments prioritize grid resilience to handle rising electricity demand and extreme weather events. Digital protection and automation upgrades further strengthen investment needs. This modernization focus remains a core driver for long-term market growth.
- For instance, ABB upgraded a national utility substation using Relion protection relays handling fault detection cycles below 20 milliseconds and supporting over 10,000 I/O signals within one control system.
Expansion of Transmission Networks and Power Interconnections
Rising electricity consumption and interregional power transfer requirements fuel transmission network expansion. Utilities build new substations to support long-distance and cross-border power flows. Integration of large generation assets requires robust substation infrastructure. Transmission corridors connecting renewable energy zones to load centers increase deployment. Power trading and grid interconnection projects strengthen demand. Substations play a central role in voltage control and system stability. This expansion trend strongly supports market growth.
- For instance, GE Vernova supplied substation equipment for a 500 kV transmission project designed to carry 3,000 MW and support fault clearing times below 40 milliseconds across interconnected grids.
Growth of Renewable Energy Integration
Large-scale renewable energy integration drives substation development. Wind, solar, and hydro projects require new grid connection points. Utility scale substations enable voltage transformation and grid synchronization. Variable generation increases demand for advanced protection and control systems. Utilities deploy substations to manage intermittency and maintain stability. Renewable energy targets accelerate infrastructure investment. This clean energy transition remains a key growth driver.
Key Trends and Opportunities
Rising Adoption of Gas-Insulated and Compact Substations
Utilities increasingly deploy gas-insulated substations in urban and space-constrained areas. GIS solutions reduce footprint while offering high reliability. Urbanization and land constraints accelerate adoption. Compact substations support underground and indoor installations. This trend creates opportunities for suppliers offering space-efficient designs. Growth in metropolitan grid upgrades supports continued demand. GIS adoption expands market opportunities.
- For instance, Mitsubishi Electric delivered a 300 kV gas-insulated substation featuring a compact bay design with busbar heights under 6.5 meters and rated continuous current capacity of 4,000 A, supporting high-density urban transmission networks.
Integration of Digital and Smart Substation Technologies
Digital substations gain traction across utility networks. Advanced sensors, communication systems, and automation improve monitoring and control. Utilities adopt digital substations to enhance reliability and reduce maintenance. Real-time data supports predictive maintenance and faster fault response. Smart grid initiatives drive adoption of digital solutions. Vendors offering integrated digital platforms gain competitive advantage. This trend opens new growth avenues.
- For instance, Schneider Electric implemented a digital substation using IEC 61850 process bus architecture, enabling protection response times below 10 milliseconds and integrating more than 5,000 real-time data points within a single control system.
Key Challenges
High Capital Investment and Long Project Timelines
Utility scale substations require significant upfront capital investment. Projects involve complex engineering and long approval cycles. Budget constraints delay execution in some regions. Land acquisition and regulatory clearances extend timelines. Utilities must balance cost with performance and reliability. Long project durations slow market turnover. Capital intensity remains a major challenge.
Complex Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
Substation projects face strict regulatory and environmental requirements. Compliance with safety, land use, and emission standards increases complexity. Permitting delays affect project schedules. GIS substations face scrutiny over gas handling and environmental impact. Utilities must address community and environmental concerns. Regulatory complexity increases development risk. This challenge affects deployment speed.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds a market share of 26.4% in the Utility Scale Substation market. Demand is driven by grid modernization and replacement of aging transmission and distribution infrastructure across the United States and Canada. Utilities invest in new substations to improve reliability, resilience, and outage management. Growth in renewable energy integration and cross-state power transfer increases substation upgrades. Expansion of data centers and electrification initiatives also support demand. Advanced automation and digital protection systems gain wider adoption. Stable regulatory frameworks and sustained utility spending support steady regional market growth.
Europe
Europe accounts for 23.8% of the global Utility Scale Substation market share. Strong focus on energy transition and decarbonization drives investments in transmission and distribution substations. Countries such as Germany, France, and the United Kingdom upgrade substations to support renewable integration and cross-border power flows. Aging infrastructure replacement remains a key driver. Urbanization increases adoption of compact and gas-insulated substations. Strict grid reliability and safety standards influence procurement. Ongoing interconnection projects and smart grid initiatives sustain regional market expansion.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific leads the market with a share of 34.7%. Rapid urbanization, industrial growth, and rising electricity demand drive large-scale substation deployment across China, India, Japan, and Southeast Asia. Governments invest heavily in transmission expansion and grid reinforcement. Integration of renewable energy and development of ultra-high-voltage corridors increase substation installations. Growing electrification and infrastructure development support sustained demand. Cost-effective construction and large project pipelines position Asia Pacific as the dominant and fastest-growing regional market.
Latin America
Latin America holds a market share of 8.1% in the Utility Scale Substation market. Growth is supported by grid expansion and renewable energy projects in Brazil, Mexico, and Chile. Utilities invest in substations to improve reliability and reduce transmission losses. Expansion of wind and solar capacity increases demand for new grid connection points. Budget constraints slow large-scale deployments, but ongoing infrastructure upgrades sustain moderate growth. Regulatory reforms and regional power integration projects support long-term market development.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for 7.0% of the global market share. Demand is driven by power infrastructure expansion in Gulf countries and electrification efforts across Africa. Large transmission projects and renewable energy developments increase substation installations. Utilities deploy substations to support industrial zones, urban growth, and grid stability. Harsh environmental conditions drive demand for robust and reliable designs. Long-term energy diversification plans and infrastructure investments support steady regional market progress.
Market Segmentations:
By Type
- Transmission substations
- Distribution substations
By Insulation
- Air-insulated substations (AIS)
- Gas-insulated substations (GIS)
By Voltage Level
- High voltage
- Extra high voltage
- Ultra-high voltage
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
Competitive landscape analysis highlights a capital-intensive and technology-driven market led by Siemens Energy, ABB Ltd., Schneider Electric, General Electric, Hitachi Energy, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Eaton Corporation, Larsen & Toubro, Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions, and Hyundai Electric & Energy Systems. These players compete through turnkey EPC capabilities, advanced protection and control systems, and strong relationships with utilities and transmission operators. Leading companies focus on high-voltage and extra-high-voltage substations, digital automation, and reliability upgrades to support grid modernization. Investments in gas-insulated and compact substations address space constraints in urban areas. Global vendors leverage scale, engineering depth, and lifecycle services, while regional firms compete through localized manufacturing and cost efficiency. Strategic partnerships, long-term utility contracts, and participation in renewable integration and interconnection projects remain central to competitive positioning in the Utility Scale Substation market.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Siemens Energy
- ABB Ltd.
- Schneider Electric
- General Electric
- Hitachi Energy
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Eaton Corporation
- Larsen & Toubro
- Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions
- Hyundai Electric & Energy Systems
Recent Developments
- In November 2024, Schneider Electric shared new “Virtual Substations” updates at Enlit 2024. Schneider also highlighted PowerLogic T300 RTU virtualization on the E4S platform.
- In May 2024, Siemens Energy announced a grid-expansion deal with Energinet. The scope covers high-voltage substation equipment for Denmark’s transmission upgrades.
- In April 2024, Hitachi Energy has secured an order from SP Energy Networks to design and implement an innovative power quality solution aimed at stabilizing the grid and enhancing the transmission of renewable energy from Scotland to England.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Insulation, Voltage Level and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Grid modernization programs will continue to drive substation upgrades.
- Renewable energy integration will increase demand for new substations.
- Digital and automated substations will gain wider utility adoption.
- Gas-insulated substations will see higher deployment in urban areas.
- Transmission expansion will remain a key investment focus for utilities.
- Aging infrastructure replacement will support steady market demand.
- Asia Pacific will maintain leadership in new substation installations.
- Grid resilience and reliability investments will shape procurement priorities.
- EPC partnerships will play a critical role in large-scale projects.
- Competition will intensify through technology, service quality, and execution capability.




