Market overview
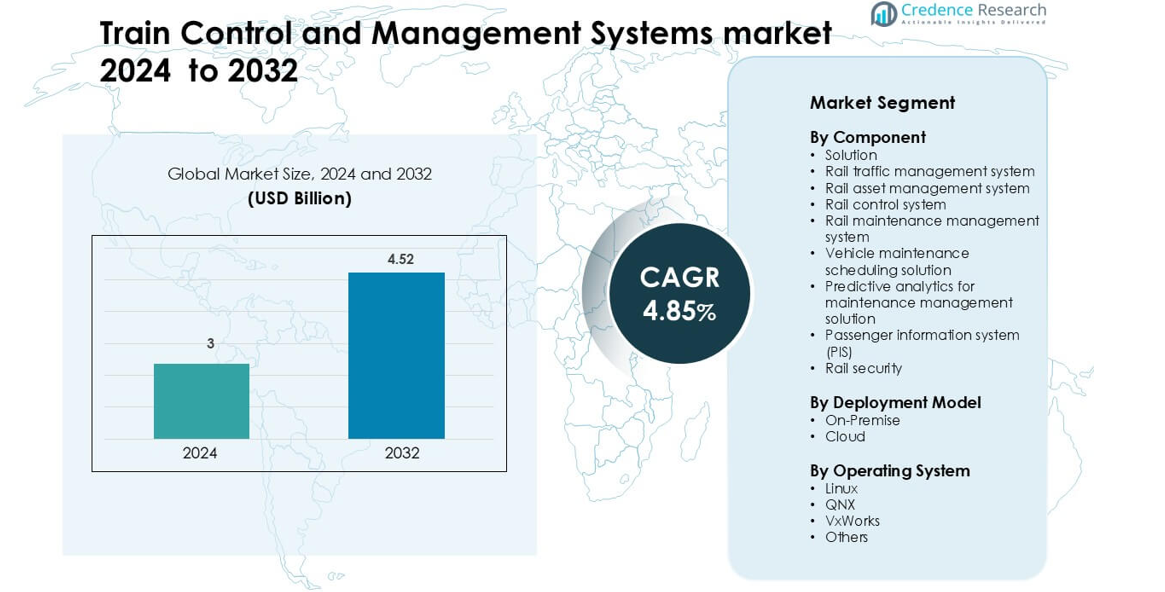
Train Control and Management Systems market was valued at USD 3 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 4.52 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 4.85 % during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Train Control and Management Systems Market Size 2024 |
USD 3 billion |
| Train Control and Management Systems Market, CAGR |
4.85% |
| Train Control and Management Systems Market Size 2032 |
USD 4.52 billion |
The Train Control and Management Systems market is shaped by major players such as Hitachi Rail, Cisco Systems, Indra Sistemas, Toshiba, ABB, Thales, Huawei Technologies, Siemens Mobility, IBM, and Alstom. These companies compete through advanced signaling systems, integrated control platforms, real-time diagnostics, and cybersecurity-enhanced communication networks. Their solutions support automated operations, predictive maintenance, and high-capacity metro corridors. Europe leads the market with a 36% share, driven by strong regulatory frameworks, extensive ETCS deployment, and continuous investment in high-speed and urban rail modernization. Strong vendor–operator partnerships and digital rail programs further strengthen regional leadership.
Market Insights
- The market reached USD 3 Billion and is set to hit USD 4.52 Billion by 2032, growing at a 4.85% CAGR, supported by rising adoption of automated rail control platforms.
- Demand grows as operators invest in real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and CBTC-based automation that improve safety and reduce operational delays.
- Digital twins, IoT-enabled sensors, and cloud analytics shape emerging trends as rail networks shift toward data-driven operations across metros and high-speed corridors.
- Competition intensifies among global players offering interoperable control systems, integrated signaling, and secure communication networks tailored for modernization and expansion cycles.
- Europe leads with a 36% share, followed by North America at 32% and Asia Pacific at 28%, while the Solution segment dominates components with a 44% share, driven by integrated control and automation demand.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Component
Solution remains the dominant sub-segment with a 44% share, supported by strong demand for integrated rail control, monitoring, and passenger-facing applications. Rail operators prefer unified platforms because these systems reduce downtime, streamline communication, and improve safety across high-density corridors. Passenger information systems and rail security tools gain traction as networks digitize real-time travel updates and strengthen threat detection. Predictive analytics and maintenance scheduling expand as operators shift toward condition-based asset management. Growth across all components is driven by modernization programs, rising urban ridership, and the push for automation in national rail upgrades.
- For instance, Siemens Mobility supplies its Trainguard MT communications-based train control (CBTC) to many metros; the system supports fully automated train circulation and has been deployed on.
By Deployment Model
On-premise deployment leads this segment with a 63% share, driven by strict data-sovereignty requirements and the need for localized control in mission-critical rail environments. Rail agencies prefer on-premise systems because they support low-latency operations and comply with national safety standards. Cloud deployment grows steadily as operators adopt remote diagnostics, scalable data storage, and centralized monitoring. Hybrid models gain interest where regulators allow selective cloud integration. Adoption across both models is shaped by cybersecurity investments, IT modernization targets, and rising demand for unified rail-operations visibility.
- For instance, Hitachi Rail’s HMAX platform, deployed on over 2,000 trains and across thousands of kilometers of signalling infrastructure, uses an “edge-to-cloud” architecture critical data is processed locally on-board via NVIDIA IGX hardware, while summary analytics are sent back to a central control system.
By Operating System
Linux dominates this segment with a 48% share, supported by its open-source architecture, strong security profile, and high customization flexibility for rail-grade embedded systems. Rail control vendors rely on Linux to support safety-critical functions, high-speed data processing, and long lifecycle management. QNX and VxWorks remain relevant for real-time operating needs, especially in automatic train protection and onboard control units. Other platforms serve niche legacy fleets that require specific integration layers. Drivers include rising demand for interoperable control systems, enhanced cybersecurity, and scalable operating environments for modern rolling stock.
Key Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Rail Network Modernization
Rail authorities upgrade legacy systems to improve safety, punctuality, and multi-line coordination. Governments invest in advanced signaling, automated train control, centralized traffic management, and digital communication systems to handle higher passenger volumes. Modernization programs also include real-time diagnostics, reduced headways, and automatic route adjustments to support dense urban rail corridors. High-speed rail expansions further push operators to adopt intelligent control systems with faster processing and integrated fail-safe features. As cities expand and intercity travel rises, modernization becomes essential for network reliability and capacity improvement. These upgrades create long-term demand for integrated Train Control and Management Systems across both new builds and retrofits.
- For instance, Deutsche Bahn (DB) signed a long-term framework with Hitachi Rail, Alstom, Siemens Mobility and others to supply 15,500 modern digital interlocking / ETCS control units by 2028.
Growing Emphasis on Safety, Compliance, and Automation
Safety remains a central priority as rail networks operate at higher speeds and face rising traffic density. Operators adopt systems that reduce human error, automate braking, manage speed limits, and detect track obstacles. Regulatory agencies mandate compliance with advanced safety standards such as automatic train protection (ATP) and communication-based train control (CBTC). These requirements push operators toward digital oversight platforms that respond faster than manual systems. Automation also enhances punctuality by enabling optimized train spacing and coordinated routing. As nations shift toward fully automated and driverless rail operations, advanced control systems become the backbone for safe, precise, and compliant network operations.
- For instance, Alstom’s Urbalis 400 CBTC system is deployed over more than 1,200 km of metro lines globally, helping reduce train headways to as little as 60 seconds while maintaining operational availability.
Expansion of Predictive Maintenance and Asset Optimization
Rail fleets depend on continuous monitoring to reduce breakdowns, extend equipment life, and improve scheduling. Predictive analytics allows operators to analyze vibration, temperature, and performance data to detect failures before they occur. With maintenance accounting for a large share of operational cost, analytics-driven models deliver notable savings and boost fleet availability. Operators integrate control systems with sensors across braking, propulsion, and door systems to capture real-time data. This data-driven approach supports better planning, reduces downtime, and strengthens overall reliability. As networks grow more digital, demand for predictive maintenance features within Train Control and Management Systems accelerates rapidly.
Key Trend & Opportunity
Integration of IoT, Edge Computing, and Digital Twins
Rail operators increasingly adopt IoT-enabled sensors, edge processing units, and digital twin models to boost responsiveness and optimize operations. IoT networks provide real-time visibility into traction, braking, signaling, passenger load, and energy use. Edge computing reduces latency during safety-critical decisions such as emergency braking or speed adjustments. Digital twins allow operators to simulate rail conditions, test route changes, and predict system behavior before real deployment. These technologies create opportunities for vendors offering scalable platforms that merge analytics, automation, and simulation. As digitalization accelerates, integrated TCMS architectures become key enablers for smart rail ecosystems.
- For instance, KONUX, known for its IoT-based predictive maintenance, initially instrumented 650 railway switches for Deutsche Bahn using IIoT sensors, and then expanded to monitor 3,500 assets across busy routes, feeding data into its analytics platform.
Rapid Shift Toward CBTC and Autonomous Train Operations
The global adoption of communication-based train control opens new growth avenues for vendors delivering advanced onboard and wayside systems. CBTC supports shorter intervals between trains, boosts line capacity, and improves energy efficiency through smoother acceleration profiles. Autonomous train operation (Grades of Automation 2–4) also expands opportunities for suppliers of real-time control logic, redundancy systems, and safety modules. Cities building new metro lines design them with automation at the core, while older systems begin phased retrofits. This transition creates strong long-term demand for TCMS platforms that support continuous communication and high-precision movement authority management.
- For instance, Alstom’s Urbalis CBTC is deployed on 190 metro lines in 32 countries, of which 67 lines operate in Grade of Automation 4 (fully driverless).
Key Challenge
High Implementation Costs and Integration Complexity
Deploying advanced control and management systems requires heavy investment in signaling upgrades, communication networks, onboard hardware, and staff training. Older rail networks face additional challenges integrating new digital modules with outdated infrastructure. These upgrades often require extended line closures or phased implementation, which increases cost and disrupts operations. Vendors must also comply with stringent safety and interoperability standards, further raising customization and certification expenses. Smaller operators struggle to justify the financial burden, which slows adoption in cost-sensitive regions. The complexity of aligning multiple stakeholders—vendors, regulators, and operators—adds further pressure on deployment timelines.
Cybersecurity Risks in Highly Connected Rail Networks
As rail systems shift toward cloud-based monitoring, IoT devices, and wireless signaling, cybersecurity threats escalate. Unauthorized access or system breaches can disrupt routing, compromise safety-critical functions, or halt network operations. Operators must secure thousands of endpoints—from onboard controllers to wayside sensors—against evolving threats. Implementing encryption, intrusion detection systems, and rapid patching adds operational complexity and cost. Many older networks lack foundational digital security frameworks, making upgrades difficult. Ensuring end-to-end protection across mixed legacy and modern systems becomes a major challenge, especially when meeting regulatory mandates for secure rail operations.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the 32% share of the Train Control and Management Systems market, driven by strong investments in automated signaling, advanced traffic management, and predictive maintenance programs. The U.S. modernizes commuter and freight corridors with CBTC adoption and integrated onboard control platforms. Canada upgrades rolling stock with real-time diagnostics and safety-critical communication tools. Rail operators favor high-reliability systems that support long-distance freight operations and dense metro networks. Cybersecurity and asset optimization tools gain momentum as digital integration expands. Regional growth remains steady due to stable funding cycles and continuous rail infrastructure modernization.
Europe
Europe leads the market with a 36% share, supported by extensive deployment of ETCS, CBTC, and automated control systems across national and cross-border corridors. Countries such as Germany, France, and the UK invest in digital traffic control, high-speed rail upgrades, and centralized fleet management platforms. Urban metros adopt advanced automatic train operation to improve frequency and safety. Sustainability policies encourage operators to shift toward energy-optimized driving solutions and predictive maintenance. Strong regulatory frameworks and interoperability standards accelerate adoption, making Europe a hub for next-generation TCMS technologies and vendor innovation.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific accounts for a 28% share, driven by rapid urban rail expansion, high-speed rail construction, and rising investments in digital control infrastructure. China and Japan lead adoption with wide use of automated train control, sophisticated signaling systems, and integrated communication networks. India accelerates modernization of metro and intercity routes with real-time monitoring, passenger information systems, and centralized control rooms. Southeast Asian countries implement digital upgrades to manage rising passenger volumes. The region grows quickly due to government-funded transportation programs, large rolling-stock fleets, and strong demand for reliable, high-capacity rail systems.
Latin America
Latin America holds a 2% share, with growth led by metro modernization, new urban rail projects, and selective adoption of automated control features. Brazil, Mexico, and Chile upgrade signaling networks and integrate passenger information and security systems to enhance operational efficiency. Budget constraints limit large-scale adoption, but targeted investments in digital monitoring and safety automation support gradual progress. Regional operators prioritize technologies that improve punctuality and reduce maintenance costs. Partnerships with global suppliers help accelerate modernization, especially in metro systems facing rising urban commuter demand.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region represents a 2% share, supported by major metro and intercity rail projects in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar. These countries deploy advanced signaling, CBTC-based driverless metro systems, and integrated fleet management solutions. Africa progresses more slowly due to funding limits, but nations such as South Africa upgrade rail safety and adopt limited digital monitoring tools. Large-scale national development plans in the Gulf drive demand for high-automation systems, predictive maintenance platforms, and centralized traffic control. Growing smart-city initiatives further strengthen adoption of integrated TCMS solutions.
Market Segmentations:
By Component
- Solution
- Rail traffic management system
- Rail asset management system
- Rail control system
- Rail maintenance management system
- Vehicle maintenance scheduling solution
- Predictive analytics for maintenance management solution
- Passenger information system (PIS)
- Rail security
By Deployment Model
By Operating System
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the Train Control and Management Systems market features strong participation from global rail technology leaders that focus on automation, digital integration, and safety-critical innovation. Companies such as Siemens Mobility, Hitachi Rail, Alstom, and Thales strengthen their position by supplying advanced signaling platforms, onboard control units, and communication-based train control solutions for both new and upgraded networks. Cisco Systems, Huawei Technologies, and IBM expand their role through communication networks, cybersecurity tools, and analytics-driven monitoring systems. Indra Sistemas, ABB, and Toshiba enhance competitiveness with integrated traffic management, power automation, and predictive maintenance capabilities. Vendors increasingly develop interoperable systems that support high-speed corridors, driverless metro operations, and condition-based maintenance. Strategic partnerships, R&D investments, and long-term supply contracts with metro operators and national rail agencies shape the competitive environment, while firms compete on reliability, lifecycle cost, and compliance with evolving safety standards.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In June 2025, ABB announced a new electric-drive marine motor, signalling crossover from rail to other transport segments; shows ABB’s broader mobility tech extension.
- In September 2024, Hitachi Rail announced integration of Communications Based Train Control (CBTC) with 5G communications for programmes in New York and Hong Kong.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Component, Deployment Model, Operating System and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Adoption of automated and driverless train operations will increase across major metro networks.
- Rail operators will expand predictive maintenance programs to improve fleet availability.
- Digital twins will support real-time simulation, asset planning, and operational optimization.
- Communication-based train control upgrades will accelerate on both new and legacy rail lines.
- Cybersecurity investment will rise as rail networks become more connected and data-driven.
- Cloud-enabled traffic management and monitoring platforms will gain wider deployment.
- Interoperable control architectures will become standard to meet cross-border and multi-vendor requirements.
- Rail agencies will prioritize energy-efficient driving and eco-optimized control algorithms.
- Integration of IoT sensors across rolling stock and infrastructure will expand rapidly.
- Strategic partnerships between rail operators and technology providers will shape long-term system innovation.




