Market Overview
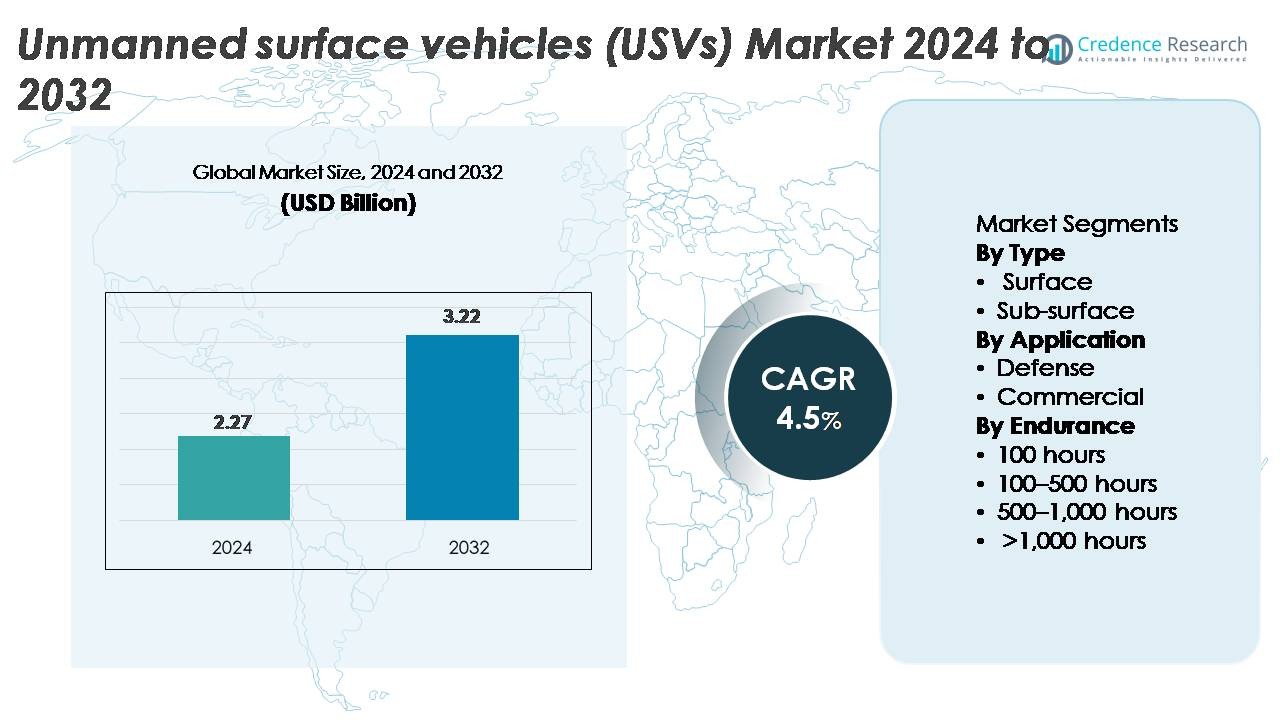
The global unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) market was valued at USD 2.27 billion in 2024 and is projected to expand to USD 3.22 billion by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% over the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs) Market Size 2024 |
USD 2.27 Billion |
| Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs) Market, CAGR |
4.5% |
| Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs) Market Size 2032 |
USD 3.22 Billion |
The USVs market is shaped by a strong mix of defense contractors, marine robotics innovators, and autonomous system providers. Key players including OceanAlpha, BAE Systems, Liquid Robotics, ECA Groupe, Fugro, Maritime Robotics AS, 5G International Inc., Kongsberg Maritime, L3Harris Technologies, and Elbit Systems Ltd. compete by advancing multi-mission platforms, AI-enabled navigation, and long-endurance propulsion systems. These companies focus on modular payload integration, autonomous mission management, and sensor-rich designs to support both defense and commercial applications. North America leads the global USVs market with a dominant 40% share, driven by large-scale naval modernization, high defense spending, and strong technological innovation ecosystems that accelerate rapid deployment of unmanned maritime systems.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) market reached USD 2.27 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 3.22 billion by 2032, registering a CAGR of 4.5% during the forecast period.
- Strong market growth is driven by rising investments in maritime security, ISR modernization, offshore energy surveys, and environmental monitoring, with surface USVs holding the dominant ~80% share due to broader mission flexibility and higher procurement volumes.
- Key trends include increasing adoption of long-endurance autonomous platforms, multi-vehicle swarm operations, AI-driven navigation, and expanding use in offshore wind, port automation, and oceanographic research across major economies.
- Competitive activity remains high, with companies such as OceanAlpha, L3Harris, BAE Systems, Kongsberg Maritime, Fugro, and ECA Groupe advancing modular designs, hybrid propulsion, and mission autonomy despite restraints related to regulatory uncertainty, navigation compliance, and cybersecurity risks.
- Regionally, North America leads with ~40% share, followed by Europe at ~30% and Asia-Pacific at ~23%, driven by naval modernization, offshore infrastructure growth, and expanding autonomous maritime operations.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Type
Surface USVs dominate the market with an estimated 78–80% share, driven by their wide deployment across naval surveillance, hydrographic surveying, port security, and environmental monitoring. Their larger payload capacity, modular sensor integration, and operational stability make them the preferred platform for defense and commercial programs. Sub-surface USVs, while smaller in share, are gaining interest for mine countermeasures and underwater inspections. Growth in this segment is supported by advancements in compact propulsion systems and improved acoustic communication, but surface vehicles remain the primary revenue generator due to higher procurement volumes and broader mission adaptability.
- For instance, Maritime Robotics’ Otter Pro USV supports a 30 kgpayload, operates for up to 20 hours (at 2 knots), and integrates high-resolution multibeam sonars for coastal hydrographic missions, demonstrating the operational scalability of modern surface platforms.
By Application
Defense applications account for the dominant around 72–75% market share, propelled by rising investments in maritime domain awareness, autonomous patrolling, anti-submarine support, and intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) missions. Naval modernization programs increasingly prioritize unmanned surface fleets to reduce operator risk and expand persistent monitoring capabilities. Commercial applications are growing steadily, driven by offshore energy inspections, environmental data collection, and port automation. However, defense maintains leadership due to large-scale procurement contracts, multi-mission payload integrations, and continuous development of autonomous navigation and threat-response systems tailored for military maritime operations.
- For instance, L3Harris’ C-Worker 15 USV is a 15-meter autonomous platform with endurance exceeding 20 days and supports advanced radar, AIS, EO/IR, and autonomous navigation systems for naval ISR and ocean-survey missions. The vessel carries large modular payloads for hydrography and subsea mapping, though specific capacities remain proprietary rather than 10-tonne class.
By Endurance
USVs with 100–500 hours endurance represent the largest segment with approximately 40–45% market share, balancing mission duration, fuel efficiency, and payload flexibility for defense patrols and commercial survey operations. Systems under 100 hours serve short-range tasks but remain limited by operational radius. Platforms offering 500–1,000 hours and >1,000 hours endurance are gaining traction for open-ocean surveillance, long-range scientific research, and persistent intelligence missions. Growth in ultra-long-endurance USVs is driven by improvements in hybrid propulsion, solar-assisted power systems, and autonomous navigation algorithms, but mid-range endurance remains dominant due to broad mission compatibility.
Key Growth Drivers
Expansion of Maritime Security and ISR Modernization Programs
Global naval forces are rapidly expanding their maritime security and intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities, creating a sustained demand surge for unmanned surface vehicles. Defense agencies increasingly prioritize autonomous maritime assets to extend surveillance coverage, reduce personnel exposure, and strengthen response capacity across contested waters. USVs equipped with radar, EO/IR sensors, AIS modules, and electronic warfare systems enable persistent monitoring without continuous manned deployment. Nations with large coastlines particularly in the Indo-Pacific and North Atlantic are accelerating investments in autonomous fleets to counter piracy, illegal fishing, smuggling, and intrusion threats. The shift toward distributed maritime operations also supports the use of USVs as communication relays, decoys, and force multipliers. Combined with increased defense budgets and multiyear procurement programs, maritime modernization remains a foundational catalyst driving USV adoption across tactical, operational, and strategic naval domains.
- For instance, Elbit Systems’ Seagull USV supports multi-mission naval operations with an endurance of over 4 days, a mission range of 1,900 km, and the ability to deploy a towed sonar array for anti-submarine warfare capabilities validated in NATO exercises.
Rising Offshore Energy, Hydrographic Survey, and Environmental Monitoring Needs
Commercial sectors are adopting USVs at an accelerated pace to meet growing requirements for seabed mapping, oceanographic research, offshore infrastructure inspection, and environmental compliance monitoring. Offshore wind developers, oil & gas operators, and marine survey companies prefer USVs for their ability to perform high-resolution acoustic mapping, subsea pipeline assessment, and bathymetric surveys at a fraction of the cost of crewed vessels. Their endurance, maneuverability, and ability to operate continuously in rough conditions significantly improve survey efficiency. The rising number of offshore wind projects especially in Europe, East Asia, and North America has intensified demand for autonomous platforms capable of long-duration data collection and near-real-time reporting. Environmental agencies also deploy USVs for pollution tracking, water quality analysis, and climate research, further broadening adoption. As regulatory pressure increases for safer, cleaner, and low-disruption marine operations, commercial industries continue shifting toward autonomous surface platforms.
- For instance, Fugro’s Blue Essence USV typically operates at a survey speed of 4 knots (around 7.4 km/h). It deploys the Blue Volta eROV which is rated for depths up to 450 meters, and maintains fully remote control from shore-based centers via a robust 4G/VSAT/Iridium hybrid link, enabling offshore inspection campaigns with an endurance of up to 10-17 days without refueling.
Technological Advancements in Autonomy, Navigation, and Hybrid Propulsion
Rapid advancements in AI-based navigation, collision avoidance, and mission automation are transforming the operational value of USVs across sectors. Modern platforms integrate multi-sensor fusion, GNSS-denied navigation, adaptive route planning, and real-time situational awareness, enabling complex missions with minimal human oversight. Parallel progress in hybrid-electric propulsion, solar-assisted power systems, and low-noise energy modules is extending mission endurance and reducing operational costs. Modular payload architectures allow seamless integration of sonar, LiDAR, communications pods, and weaponized systems for defense use. Vendors are also introducing scalable hull designs and interoperable command-and-control systems that comply with emerging maritime autonomy standards. These connected technology improvements enhance reliability, mission flexibility, and safety, making USVs increasingly attractive as substitutes for crewed vessels in challenging or repetitive maritime tasks. The compounding effect of autonomy and propulsion innovation remains one of the strongest structural drivers in this market.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Growth of Collaborative and Swarm-Based Autonomous Maritime Operations
Swarm autonomy and multi-vehicle cooperative missions are emerging as transformative opportunities in the USVs market. Defense agencies are testing connected USV groups capable of synchronized patrolling, mine detection, perimeter defense, and distributed sensing. These systems reduce single-asset vulnerability and dramatically expand mission reach across large maritime areas. Commercial operators also see potential in multi-USV survey fleets that accelerate data acquisition for offshore wind site characterization, seabed mapping, and environmental monitoring. Advances in secure mesh networking, shared situational awareness, and decentralized decision-making are enabling more resilient and scalable autonomous operations. The trend aligns with broader shifts toward unmanned-manned teaming and distributed maritime logistics, creating new opportunities for system integrators and software developers specializing in autonomy algorithms, cross-platform communication, and fleet orchestration tools.
· For instance, NATO’s CMRE demonstrated coordinated mine-countermeasure missions using the MUSCLE autonomous underwater vehicle, which operated with high-frequency synthetic-aperture sonar to deliver wide-area seabed imaging during multi-system trials in European waters. The trials validated cooperative behaviors across unmanned surface and underwater assets without relying on a single-vessel platform.
Increasing Integration of USVs into Smart Ports and Maritime Logistics
Smart port modernization is opening significant opportunities for USVs in security patrolling, autonomous cargo escorting, hull inspection, dredging support, and navigational hazard monitoring. As ports adopt digital infrastructure including IoT sensors, AI-driven traffic management, and automated terminals USVs function as mobile data collectors and safety enablers. Their ability to operate continuously, detect anomalies, and transmit real-time situational information enhances port efficiency and reduces manual labor dependence. Additionally, commercial shipping companies are exploring USVs for autonomous towing, last-mile cargo movement within harbors, and remote pilotage support. These applications align with global goals to reduce emissions, optimize port traffic, and improve operational safety. As more port authorities invest in automation and digital twins, USVs are positioned to become critical components of next-generation maritime logistics ecosystems.
Strong Opportunity in Long-Endurance and Renewable-Energy-Powered USVs
A growing trend toward persistent ocean monitoring and extended offshore missions is driving demand for USVs powered by renewable and hybrid systems. Platforms utilizing solar panels, wave energy converters, and hydro-generators can remain at sea for months, significantly reducing fuel consumption and operational costs. These long-endurance vehicles are highly valued for climate research, maritime surveillance, and deep-ocean acoustic monitoring. As countries expand marine protected areas and environmental data mandates, renewable-energy-powered USVs offer a scalable and sustainable solution. Technological advancements in battery density, corrosion-resistant materials, and autonomous power management systems are further enhancing mission duration and reliability. This trend opens strong opportunities for vendors developing ultra-long-endurance platforms tailored for environmental science, defense reconnaissance, and offshore asset monitoring.
- For instance, Saildrone’s Explorer USV operates on solar and wind energy and has completed missions exceeding 370 days without refueling, collecting continuous oceanographic and meteorological data across remote regions.
Key Challenges
Navigation Regulations, Collision Avoidance, and Maritime Legal Barriers
Despite rapid adoption, regulatory uncertainties remain a major obstacle for USV deployment. International maritime laws especially those governing autonomous navigation, vessel identification, collision avoidance, and radiofrequency use are still evolving, creating operational constraints for cross-border missions. Ensuring compliance with COLREGs (International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea) is particularly complex for fully autonomous vessels that rely on sensor fusion and AI decision-making. Many port authorities also lack standardized frameworks for approving unmanned surface operations, leading to delays in commercial adoption. Privacy concerns, maritime security rules, and liability issues related to accidents or system malfunctions further complicate deployment. These regulatory and legal limitations significantly slow the scalability of autonomous maritime fleets and require coordinated international policy development.
Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities and Interference Risks in Autonomous Maritime Systems
As USVs rely heavily on digital communication, remote control, and sensor-based data exchange, cybersecurity risks present one of the most pressing challenges. GPS spoofing, signal jamming, unauthorized system intrusion, and data manipulation can compromise mission integrity and lead to severe operational failures. Defense and commercial operators face increasing threats as adversaries develop more sophisticated cyberattack methods targeting maritime assets. Ensuring robust encryption, secure communication protocols, onboard AI anomaly detection, and hardened command-and-control systems is essential but adds significant cost and engineering complexity. Additionally, long-endurance USVs operating far from human oversight must maintain cybersecurity resilience over extended periods, making threat mitigation even more difficult. Cyber risks remain a critical barrier to scaling autonomous maritime operations globally.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the leading position in the USVs market with around 38–40% share, supported by strong defense procurement, extensive coastline security initiatives, and rapid adoption of autonomous maritime technologies. The U.S. Navy’s growing focus on unmanned surface fleets for ISR, mine countermeasures, and distributed maritime operations drives consistent demand. Commercial sectors including offshore energy, port surveillance, and environmental monitoring also deploy USVs for cost-efficient data collection and inspection. Increasing investments in AI-driven navigation, large defense modernization budgets, and collaborations with leading autonomy developers reinforce North America’s dominant role in global USV deployment.
Europe
Europe accounts for approximately 28–30% of the global market, driven by high adoption across maritime security, offshore wind development, hydrographic surveying, and environmental research. The region’s expanding offshore wind installations in the U.K., Germany, and the Netherlands significantly boost USV demand for seabed mapping and asset inspection. European naval forces increasingly integrate autonomous surface vessels for border security and situational awareness missions in the North Sea, Baltic Sea, and Mediterranean waters. Strong regulatory support for maritime digitalization, coupled with active R&D programs in marine robotics, positions Europe as a fast-advancing USV ecosystem with diversified applications.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific represents around 22–24% of the USV market, fueled by rising naval modernization, territorial surveillance needs, and expanding offshore infrastructure. Countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and Australia are investing heavily in unmanned maritime platforms to strengthen ISR, coastal defense, and anti-intrusion capabilities. Growing offshore oil, gas, and renewable energy activities further support commercial deployments for survey and inspection tasks. Regional demand also benefits from advancements in domestic shipbuilding, robotics, and sensor integration. Increasing maritime tensions in the South China Sea and Indian Ocean amplify the strategic importance of autonomous surface vessels across the region.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region holds about 6–7% market share, primarily driven by maritime security needs, port protection, and offshore energy exploration. Gulf nations, particularly the UAE and Saudi Arabia, invest in USVs for patrol missions, critical infrastructure protection, and autonomous surveillance around high-value offshore assets. The region’s expanding offshore oil and gas operations require efficient inspection, environmental monitoring, and hydrographic survey capabilities, accelerating commercial USV adoption. African coastal states are gradually adopting unmanned surface technologies to enhance anti-piracy measures and monitor illegal fishing, though budget constraints limit broader regional penetration.
Latin America
Latin America accounts for approximately 4–5% of the global market, supported by increasing maritime surveillance requirements, coastal resource protection, and offshore energy developments. Brazil, Mexico, and Chile lead regional adoption as they strengthen naval capabilities and expand autonomous systems for patrol and environmental monitoring. USVs are increasingly used for offshore oilfield inspection, port security, and marine research in biodiverse ecosystems. Growth remains steady but moderate due to financial limitations and slower procurement cycles. However, rising emphasis on protecting maritime borders and monitoring illegal activities is expected to drive gradual expansion in the region’s USV utilization.
Market Segmentations:
By Type
By Application
By Endurance
- 100 hours
- 100–500 hours
- 500–1,000 hours
- >1,000 hours
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The USVs market is highly competitive, characterized by a mix of established naval contractors, marine robotics firms, and emerging autonomy technology developers. Leading companies focus on expanding modular platforms, integrating advanced ISR sensors, and strengthening autonomous navigation capabilities to meet diverse defense and commercial requirements. Firms such as L3Harris, Textron Systems, Kongsberg Maritime, Elbit Systems, and Ocean Aero invest heavily in AI-driven control software, multi-mission payloads, and long-endurance propulsion technologies to enhance operational versatility. Strategic collaborations with navies, energy companies, and research institutions further accelerate product development and large-scale deployment. Startups specializing in swarm autonomy, renewable-energy-powered vehicles, and data analytics platforms are also gaining traction, intensifying competition in niche applications. Mergers, acquisitions, and joint development programs remain common as companies seek to expand global presence, secure long-term defense contracts, and strengthen their technology portfolios. This dynamic environment supports continuous innovation and rapid commercialization of next-generation USV systems.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- OceanAlpha
- BAE Systems
- Liquid Robotics, Inc.
- ECA Groupe
- Fugro
- Maritime Robotics AS
- 5G International Inc.
- Kongsberg Maritime
- L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- Elbit Systems Ltd.
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, Fugro was awarded a contract by the Norwegian Hydrographic Service (NHS) to support the 2025 MAREANO seabed-mapping programme using USV-based surveying. Fugro will deploy its 18-meter Blue Eclipse® USV to conduct autonomous seabed mapping for the first time in the programme’s history.
- In May 2025, OceanAlpha, held its first demonstration of a USV in the Middle East, signaling expansion into new regional markets.
- In April 2025, OceanAlpha announced the launch of its L42 USV at Ocean Business 2025 a platform offering a hybrid-power system with about 1,500 km range (≈ 8 days at 4 knots), redundant motors, payload flexibility for hydrographic survey, pipeline inspection, and offshore energy applications.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Type, Application, Endurance and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Adoption of fully autonomous USV fleets will accelerate as navies shift toward distributed maritime operations and unmanned–manned teaming.
- Long-endurance platforms powered by hybrid, solar, and renewable systems will gain prominence for persistent ocean monitoring and defense reconnaissance.
- Swarm-enabled USVs will become central to mine countermeasures, coordinated patrol missions, and large-area environmental surveys.
- AI-driven navigation, sensor fusion, and collision-avoidance systems will significantly enhance mission safety and autonomous decision-making.
- Commercial sectors will expand USV use in offshore wind surveys, subsea inspections, environmental monitoring, and port automation.
- Regulatory standardization for autonomous vessel operations will progress, enabling broader cross-border deployment and operational approvals.
- Demand for modular hull designs and multi-mission payload integration will rise across defense and industrial applications.
- Cybersecurity advancements will become a critical focus to protect USVs from spoofing, jamming, and data manipulation.
- Growth in ocean research programs and climate-monitoring initiatives will increase reliance on long-duration USV missions.
- Collaboration between government agencies, research institutions, and private technology developers will accelerate innovation and global market adoption.




