Market Overview
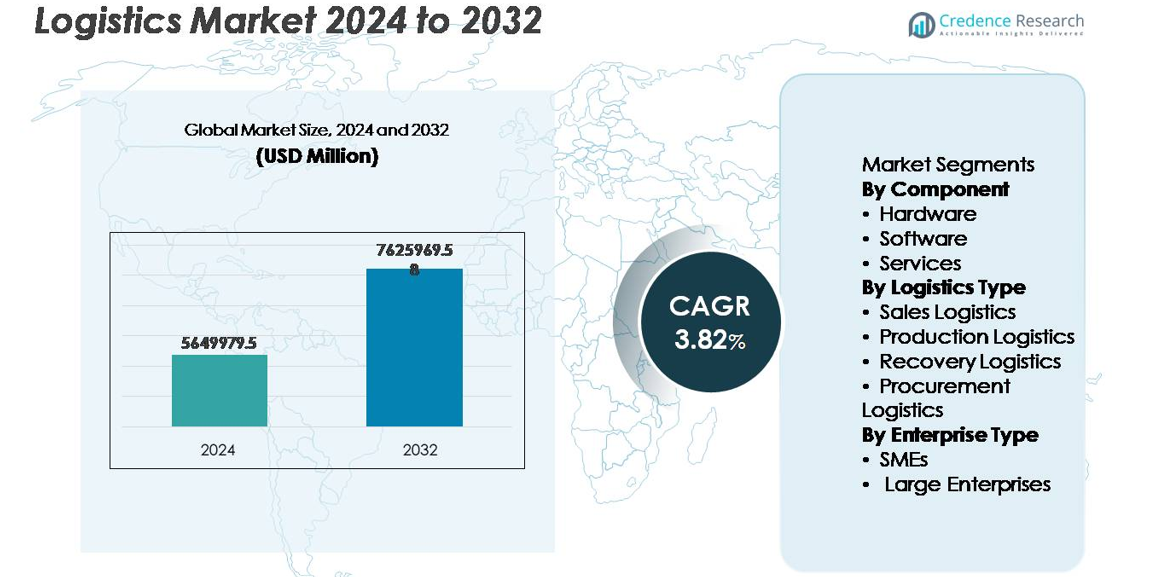
The global logistics market was valued at USD 5,649,979.5 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 7,625,969.58 million by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 3.82% over the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Logistics Market Size 2024 |
USD 5,649,979.5 million |
| Logistics Market, CAGR |
3.82% |
| Logistics Market Size 2032 |
USD 7,625,969.58 million |
The logistics market is shaped by a mix of global automation leaders and specialized system integrators, including Knapp, Murata Machinery, SSI SCHAEFER Group, Daifuku Co., Ltd., Jungheinrich AG, Honeywell International Inc., KION Group AG, Toyota Industries Corporation, TGW Logistics Group, and KUKA AG. These companies compete through warehouse robotics, autonomous material handling, data-driven fleet optimization, and integrated storage and retrieval systems. Asia-Pacific leads the logistics market with approximately 38% share, driven by large-scale manufacturing, port expansions, e-commerce penetration, and multimodal infrastructure growth. North America and Europe continue to invest heavily in automation and sustainability as part of supply chain transformation.
Market Insights
- The global logistics market was valued at USD 5,649,979.5 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 7,625,969.58 million by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of 3.82% during the forecast period.
- Market growth is driven by rising automation adoption, digitally optimized fulfillment networks, and increasing demand for e-commerce based last-mile delivery services across developed and emerging economies.
- Key trends include AI-enabled route optimization, sustainable fleet transition, multimodal digital freight platforms, and the expansion of smart warehousing powered by robotics and IoT tracking.
- Competitive dynamics are shaped by global logistics integrators and technology players focusing on resilient supply chains, though infrastructure disparity and cybersecurity risks remain significant restraints.
- Asia-Pacific dominates with around 38% share, followed by North America at 32% and Europe at 27%, while the hardware segment leads by component, supported by warehouse automation and advanced handling systems.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Component
The logistics market is segmented into hardware, software, and services, with the hardware segment holding the dominant market share, driven by the increasing adoption of advanced automation systems, barcode and RFID systems, autonomous mobile robots, and sensor-enabled tracking infrastructure. Investments in warehouse modernization and fulfillment center robotics continue to accelerate hardware demand as enterprises prioritize labor optimization, faster order processing, and accuracy improvements. Meanwhile, software platforms supporting real-time visibility, predictive analytics, and transportation management are rapidly scaling in adoption, complemented by expanding service offerings related to integration, maintenance, and managed operations.
- For instance, Zebra Technologies reported that its FX9600 fixed RFID reader is capable of processing up to 1,200 tag reads per second, supporting high-density inventory environments such as large fulfillment hubs.
By Logistics Type
Based on logistics type, the market is categorized into sales logistics, production logistics, recovery logistics, and procurement logistics. Production logistics represents the leading sub-segment, owing to the rising need for synchronized material movement, just-in-time supply processes, and factory floor integration within manufacturing ecosystems. Increased reliance on digital twins, automated production flows, and demand-driven planning models supports segment growth. Sales logistics is expanding with the surge in e-commerce fulfillment and last-mile delivery solutions, while procurement and recovery logistics benefit from circularity initiatives, reusable asset management, and reverse logistics frameworks supporting returns and recycling.
- “For instance, UPS’ automated Worldporthub in Louisville features a throughput capacity of 416,000 packages per hour across 155 miles of conveyors, demonstrating the scale of automated sales logistics fulfillment systems.”
By Enterprise Type
The market by enterprise type is divided into SMEs and large enterprises, with large enterprises dominating the segment due to higher technology spending capacity, global distribution networks, and strategic adoption of warehouse automation and robotic process workflows. Large enterprises leverage integrated logistics automation to reduce operational risk, improve real-time visibility, and enhance resilience across multi-country supply chains. However, SMEs are emerging as a high-growth adopter segment, supported by cloud-based logistics platforms, subscription-based automation tools, and scalable inventory and transport management systems that reduce upfront capital expenditure and deployment complexity.
Key Growth Drivers:
Rising Adoption of Automation and Digital Supply Chain Technologies
Automation has become a foundational driver for logistics transformation as enterprises seek greater throughput efficiency, reduced human error, and faster fulfillment cycles. Robotics, autonomous mobile vehicles, AI-enabled route optimization, and digital twin–based warehouse simulations are accelerating process modernization. Cloud-integrated transport management systems and real-time freight visibility platforms enhance decision-making, supporting cost predictability and fleet utilization. The growth of e-commerce and the need for same-day delivery models reinforce demand for scalable automation. As organizations adopt predictive asset management, advanced scanning, and contactless documentation, digital ecosystems are redefining operational reliability and customer experience. This widespread shift positions automation as a long-term enabler of competitive differentiation.
- For instance, FedEx deployed SenseAware IoT sensor technology in more than 90 countries, tracking shipment temperature, light exposure, and location data with transmission intervals as frequent as every 5 minutes, supporting pharmaceutical and high-value asset logistics.
Expansion of Global Trade Flows and Cross-Border Distribution Networks
Trade liberalization, nearshoring strategies, and regional economic integration stimulate logistics market expansion by intensifying cross-border transportation requirements. The proliferation of digital marketplaces has widened the trade participation of SMEs, leading to a surge in multi-country shipping volumes and complex customs compliance workflows. Infrastructure investments—including smart ports, warehousing clusters, multimodal hubs, and cross-border corridors—support higher throughput capacity. Vendor diversification strategies implemented in response to supply chain interruptions have increased reliance on regional inventory centers, bonded warehouses, and flexible distribution models. As emerging markets strengthen their export manufacturing capabilities, logistics providers continue scaling intelligent freight management, customs automation, and multimodal connectivity.
- For instance, Panasonic Logistics utilizes an integrated, global logistics network (including owned facilities, 3PL partners, and various sales bases across Asia and other regions) to support diversified vendor sourcing and rapid replenishment requirements for electronics components.
Growth in E-commerce, Omni-channel Retail, and Last-mile Delivery Systems
E-commerce remains a critical catalyst reshaping logistics, driven by rapid order turnaround expectations, micro-fulfillment centers, and delivery personalization. Omni-channel models require unified inventory visibility, dynamic routing, and real-time communication between fulfillment partners and consumers. The expansion of grocery delivery, subscription-based models, and urban delivery formats has boosted adoption of electrified fleets, delivery lockers, and route-optimized dispatch platforms. Retailers are forming strategic partnerships with logistics technology providers to manage cost per delivery and enhance reverse logistics operations. As product returns and recycling initiatives grow, logistics providers integrate reverse flow capabilities into forward networks, strengthening circular supply chains.
Key Trends and Opportunities:
Shift Toward Sustainable, Green, and Circular Logistics Models
Sustainability-driven regulations, carbon transparency mandates, and resource efficiency targets are accelerating investment in low-emission fleets, route optimization software, and green warehousing infrastructure. Electric vehicles, hydrogen-powered trucks, and alternative marine fuels are transitioning from pilots to scale deployments. Packaging minimization, reusable containers, and recycling-enabled logistics models support circular manufacturing ecosystems. Carbon accounting platforms and blockchain-based traceability tools create verifiable environmental reporting. As enterprises prioritize ESG compliance and emission reduction goals, logistics stakeholders gain opportunities in carbon-neutral delivery, eco-optimized multimodal transport, and green last-mile solutions.
- For instance, DHL has deployed more than 32,000 electric vehicles across its logistics operations, supporting emission-reduction initiatives through electrified last-mile delivery networks in over 500 global cities.
Integration of AI-enabled Predictive, Autonomous, and Intelligent Operations
AI adoption is creating opportunities for predictive planning, demand sensing, autonomous navigation, and cognitive decision support across logistics workflows. Intelligent transport systems predict weather disruptions, congestion, and asset downtime, enabling proactive risk mitigation. Autonomous drones, robotic picking, and self-driving freight vehicles are progressing from test environments into commercial logistics corridors. AI-powered simulation improves warehouse layout efficiency and throughput planning. The fusion of computer vision, machine learning, and IoT sensors continues enhancing freight condition monitoring, safety compliance, and inventory accuracy. These advancements present significant opportunities for efficiency-driven logistics transformation.
- “For instance,Amazon has deployed more than 1,000 AI-enabledRobin robotic arms across its network to sort packages, and has introduced the Sparrow picking system, its first robot capable of identifying and handling millions of diverse, individual product SKUs (approximately 65% of the total catalog), supporting high-volume fulfillment operations”
Key Challenges:
Infrastructure Gaps, Fragmentation, and Uneven Digital Readiness
Infrastructure disparities across transport networks and warehousing ecosystems hinder logistics scalability. Fragmentation persists, particularly among small carriers and regional operators with limited access to automation capital. Congested ports, inadequate cold chain facilities, and limited multimodal connectivity delay shipment cycles and raise operational costs. Digital readiness remains uneven, with interoperability issues between legacy systems and modern platforms restricting real-time coordination. Variable regulatory policies and customs frameworks further contribute to delay and complexity, challenging seamless cross-border integration.
Rising Cybersecurity Risks and Data Privacy Vulnerabilities
As logistics networks grow more digitally connected, the exposure to cyber threats, ransomware, and data breaches intensifies. Supply chain management platforms store sensitive partner and customer information, making them attractive targets for malicious attacks. IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and connected warehouse systems increase entry points for cyber exploitation. Lack of standardized cybersecurity frameworks and insufficient monitoring across distributed networks elevate compliance and risk mitigation costs. Data privacy regulations demand robust encryption, governance, and incident response structures, challenging logistics operators managing diverse global systems.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds approximately 32% of the logistics market share, driven by advanced warehouse automation, strong cold-chain networks, and mature third-party logistics ecosystems supporting retail, healthcare, and industrial distribution. The U.S. remains the core hub due to its expansive e-commerce activity and nationwide freight networks integrating road, air, and intermodal operations. Investment in autonomous freight vehicles, AI-enabled route optimization, and sustainable fleet transition strengthens the region’s innovation advantage. Cross-border trade with Mexico and Canada further supports multimodal expansion, particularly under nearshoring and manufacturing relocation strategies that favor local supply resiliency and reduced lead times.
Europe
Europe accounts for around 27% of the global logistics market, supported by established international trade corridors, port connectivity, and advanced regulatory frameworks governing freight safety and sustainability. The region benefits from dense urban logistics networks and investments in green transportation, electric fleets, and carbon compliance infrastructure. Germany and the Netherlands remain central logistics hubs, supported by high-volume warehouse capacity and digitally coordinated freight routes. EU circular economy policies accelerate demand for reusable packaging logistics and reverse supply flows. Ongoing challenges include rising cross-border documentation requirements and labor shortages across transport and warehousing operations.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific dominates the global logistics landscape with approximately 38% market share, driven by strong manufacturing output, rapid e-commerce penetration, and significant port and logistics infrastructure expansion. China, India, Japan, and Southeast Asian economies fuel demand through export manufacturing, industrial clusters, and resource flows supporting global supply chains. Government-backed investments in smart ports, digital customs, and multimodal freight corridors accelerate modernization. The region’s expanding middle-class consumption base propels last-mile delivery and fulfillment volume growth. However, infrastructure imbalances between urban and inland networks remain a challenge, creating opportunities for logistics automation and advanced capacity planning solutions.
Latin America
Latin America holds close to 2% market share, influenced by emerging e-commerce logistics, agrifood export channels, and regional trade alliances that support cross-border freight integration. Brazil and Mexico act as primary logistics centers with expanding warehousing and bonded distribution zones. Investments in rail connectivity, smart port development, and airport cargo handling are improving throughput capacity. Political volatility, customs delays, and inconsistent infrastructure quality across rural corridors continue to affect operational predictability and cost structures. Growth opportunities emerge in cold-chain networks, digital freight platforms, and sustainable fleet expansion targeting reduced fuel dependency.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region represents about 1% of the logistics market share, driven by energy exports, free trade zones, and rising investment in air cargo connectivity. Gulf nations are developing multimodal logistics hubs powered by bonded warehousing and customs digitization. Infrastructure corridors across Sub-Saharan Africa support agricultural and mining freight flows despite operational challenges from road quality, customs fragmentation, and technology maturity gaps. Logistics providers increasingly adopt fleet telematics, GPS tracking, and cloud platforms to enhance visibility. Strategic diversification initiatives in the Gulf region support logistics-based economic transformation and global distribution re-export models.
Market Segmentations:
By Component
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
By Logistics Type
- Sales Logistics
- Production Logistics
- Recovery Logistics
- Procurement Logistics
By Enterprise Type
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The logistics market features a highly competitive landscape characterized by global integrators, regional third-party logistics providers, freight forwarders, and technology-driven entrants reshaping service models. Established players compete through diversified multimodal networks, scalable warehousing infrastructure, and end-to-end supply chain management offerings. Strategic focus areas include automation-enabled fulfillment, AI-driven fleet optimization, carbon-efficient operations, and cross-border regulatory compliance services. Technology providers increasingly collaborate with logistics operators to deploy real-time tracking platforms, predictive analytics, digital documentation, and autonomous delivery systems. Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic alliances remain prevalent as companies expand geographic footprints and service portfolios. Rising customer expectations for transparency, faster delivery, and sustainable logistics intensify innovation, compelling organizations to adopt next-generation supply chain solutions for resilient, cost-efficient, and digitally integrated operations.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Knapp (Austria)
- Murata Machinery, Ltd (Japan)
- SSI SCHAEFER Group (Germany)
- Daifuku Co., Ltd. (Japan)
- Jungheinrich AG (Germany)
- Honeywell International Inc. (U.S.)
- KION Group AG (Germany)
- Toyota Industries Corporation (Japan)
- TGW Logistics Group (Austria)
- KUKA AG (Germany)
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, KION opened a new highly automated spare-parts distribution center (Regional Distribution Center Central Europe) in Kahl am Main.
- In February 2024, Dematic entered into a partnership with Groupe Robert, a Canadian Logistics company. The partnership aimed to open an automated cold storage facility. The facility has a high-capacity Automated Storage and Retrieval System with 130-foot tall cranes for managing frozen and fresh foods.
- In November 2023: Knapp, an automation solution provider, partnered with Biogena, an Austrian Health Product company, to automate the processing of international shipping.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Component, Logistic type, Enterprise type and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Automation and robotics will continue to transform warehousing, fulfillment speed, and workforce allocation.
- AI-driven predictive analytics will optimize demand forecasting, fleet utilization, and risk mitigation.
- Electrification and hydrogen-powered fleets will accelerate sustainable logistics and emissions reduction.
- Digital freight platforms will enhance transparency and real-time shipment collaboration.
- Autonomous vehicles and drones will expand pilot-stage operations into commercial logistics corridors.
- Blockchain-enabled traceability will support compliance, authenticity checks, and cross-border documentation.
- Smart port infrastructure will improve cargo flow, congestion management, and data connectivity.
- Circular logistics will grow through reusable packaging, reverse flows, and resource recovery.
- Edge computing and IoT sensors will strengthen asset monitoring and cold-chain reliability.
- Nearshoring and regional manufacturing shifts will reshape global distribution strategies.




