Market Overview
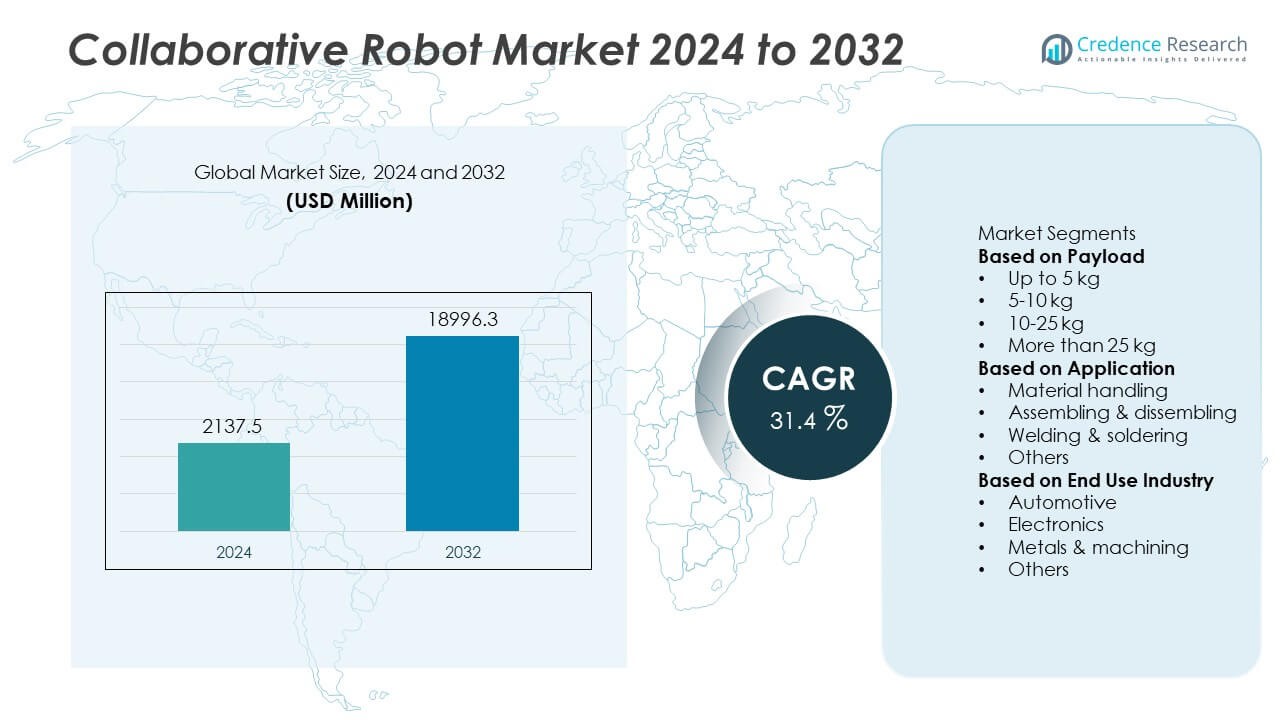
The Collaborative Robot Market reached USD 2,137.5 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 18,996.3 million by 2032, supported by a CAGR of 31.4% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Collaborative Robot Market Size 2024 |
USD 2,137.5 Million |
| Collaborative Robot Market, CAGR |
31.4% |
| Collaborative Robot Market Size 2032 |
USD 18,996.3 Million |
The Collaborative Robot market is shaped by leading companies such as Universal Robots, FANUC Corporation, ABB Ltd, KUKA AG, Yaskawa Electric Corporation, Doosan Robotics, Techman Robot Inc., AUBO Robotics, Rethink Robotics, and Nachi-Fujikoshi Corporation. These players focus on advanced sensing, higher payload capability, and flexible automation solutions that support fast deployment across manufacturing and service industries. Asia Pacific leads the global market with a 31% share, driven by large-scale manufacturing and strong automation investments. North America follows with a 33% share, supported by rapid adoption among SMEs, while Europe holds a 29% share backed by Industry 4.0 initiatives and strong automotive and electronics production.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Collaborative Robot market reached USD 2,137.5 million in 2024 and will grow to USD 18,996.3 million by 2032 at a CAGR of 31.4%.
- Demand rises as manufacturers adopt cobots for flexible automation, with the up to 5 kg payload segment leading at a 46% share due to strong suitability for small-part handling and assembly tasks.
- Key trends include rapid integration of AI, 3D vision systems, and machine learning, enabling cobots to perform precision assembly, inspection, and adaptive material handling across dynamic production environments.
- Competitive activity intensifies as companies expand product ranges, strengthen software capabilities, and form partnerships to serve automotive, electronics, logistics, and metalworking sectors, while high integration costs remain a restraint for some SMEs.
- Regionally, North America holds a 33% share, Asia Pacific accounts for 31%, and Europe holds 29%, supported by strong adoption across automotive, electronics, and high-mix manufacturing operations.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Payload
The Up to 5 kg payload segment leads the market with a 46% share, driven by strong adoption in small-part handling, light assembly, packaging, and pick-and-place operations. These cobots offer easy deployment, lower cost, and higher flexibility for SMEs seeking automation without complex infrastructures. Manufacturers prefer this range due to compact design, reduced safety requirements, and faster ROI. The 5–10 kg and 10–25 kg segments gain traction as industries automate medium-load tasks in electronics and automotive production lines. Payloads above 25 kg remain niche but expand with growing demand for heavy-duty collaborative operations in machining and material transfer.
- For instance, Universal Robots’ UR3e handles a 3 kg payload and completes cycle tasks with a repeatability of 0.03 mm. The robot supports over 500 configured applications across electronics, pharma, and packaging lines.
By Application
Material handling dominates this segment with a 41% share, supported by rapid adoption in pick-and-place, machine tending, palletizing, and packaging workflows. Manufacturers implement cobots to improve accuracy, reduce repetitive strain tasks, and increase production throughput. Assembling and disassembling applications grow as cobots assist with precision tightening, component fitting, and inspection tasks in electronics and automotive lines. Welding and soldering gain momentum due to rising use of cobots in metal fabrication, supported by improved sensors and path-control systems. Other applications expand as companies deploy cobots for quality checks, testing, and surface finishing.
- For instance, certain variants of the ABB GoFa CRB 15000 have a payload capacity of up to 14 kg (in a wrist-down configuration), a reach of up to 1.62 m (flange reach), and a maximum Tool Center Point (TCP) speed of up to 2.2 m/s. The robot series offers a best-in-class repeatability as low as 0.02 mm.
By End Use Industry
The Automotive sector leads with a 38% share, driven by rising automation in assembly lines, component handling, material movement, and robotic inspection. Automakers integrate cobots to achieve higher consistency, reduce downtime, and support flexible production across engine, body, and electronics modules. Electronics follows due to precision assembly needs and growing consumer device production, where cobots handle delicate components with reliability. Metals and machining adopt cobots for tasks such as polishing, CNC machine tending, and welding, improving worker safety and output. Other industries expand adoption as SMEs seek cost-efficient automation for packaging, logistics, and quality control.
Key Growth Drivers
Growing Adoption of Automation Among SMEs
Small and medium-sized enterprises drive strong demand for collaborative robots as they seek cost-effective automation with minimal infrastructure upgrades. Cobots offer easy programming, quick deployment, and lower integration costs than traditional industrial robots. Their ability to work safely alongside human operators enables flexible production setups and improves labor productivity. SMEs benefit from shorter payback periods and enhanced process consistency, especially in material handling, assembly, and packaging. This shift accelerates adoption across manufacturing, logistics, and service sectors, strengthening market growth.
- For instance, FANUC’s CRX-5iA cobot performs tasks with 0.03 mm repeatability and operates at a maximum speed of 1,000 mm/s. The system supports more than 25 certified plug-in software tools for handling, tending, and inspection tasks.
Rising Need for Flexible Manufacturing Systems
Manufacturers across industries adopt collaborative robots to meet rising demand for flexible, high-mix, low-volume production. Cobots allow quick reconfiguration of tasks without specialized programming skills, enabling smooth transitions between product variants and seasonal production cycles. Their compact size, mobility, and intuitive interfaces support adaptable workflows on crowded factory floors. This flexibility aligns with smart manufacturing initiatives, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency. As industries embrace Industry 4.0, cobots become essential for agile and responsive production environments.
- For instance, Yaskawa’s HC20XP cobot handles 20 kg payload tasks with a maximum reach of 1,700 mm and maintains ±0.05 mm repeatability in precision processes. The robot integrates a 6-axis design that enables flexible positioning in tight manufacturing cells.
Increasing Use of Cobots in Hazardous and Repetitive Tasks
Collaborative robots gain traction as industries automate high-risk, repetitive, and ergonomically challenging tasks to improve worker safety and reduce injury rates. Their built-in safety sensors, force-limiting systems, and precise motion control allow safe collaboration in welding, machine tending, and heavy material handling. By taking over repetitive workflows, cobots enhance accuracy, reduce defects, and maintain consistent output quality. Companies also leverage cobots to address labor shortages in roles that require precision or endurance, reinforcing their growing role across manufacturing operations.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Advancements in AI, Vision Systems, and Machine Learning
AI-enabled cobots equipped with advanced vision systems, 3D cameras, and machine-learning algorithms are transforming accuracy, path planning, and adaptive decision-making. These upgrades enable cobots to handle complex tasks such as real-time inspection, precision assembly, and dynamic object detection. Enhanced sensing capabilities allow safer human-robot collaboration and higher productivity in changing environments. Manufacturers invest in smart cobots to improve traceability, reduce errors, and support automated quality control workflows. This trend creates strong opportunities for next-generation cobots in electronics, automotive, and logistics sectors.
- For instance, Omron’s TM14 cobot integrates a built-in vision system that captures 5-megapixel images and processes 30 frames per second. The unit performs positional adjustments with 0.1 mm accuracy during assembly tasks.
Expanding Applications in Logistics, Warehousing, and Healthcare
Cobots are expanding beyond manufacturing into fast-growing sectors such as warehousing, intralogistics, and healthcare. Logistics operators deploy cobots for picking, sorting, palletizing, and order fulfillment to meet rising e-commerce volumes. Healthcare facilities use cobots for lab automation, sample handling, and assistive tasks. The versatility, compact design, and mobility of cobots allow seamless integration into non-traditional environments. This diversification creates new opportunities for vendors to offer sector-specific solutions and service-based deployment models.
- For instance, Doosan Robotics’ H2017 cobot supports logistics centers with a reach of 1,700 mm and repeatability of 0.1 mm. The cobot handles high-frequency picking cycles and interfaces with automated storage modules through its torque-controlled joints.
Key Challenges
High Integration Costs and Limited Technical Expertise
Despite lower upfront investment than industrial robots, cobot deployment still involves integration costs related to programming, peripherals, and system calibration. Many SMEs lack in-house technical expertise, slowing adoption and raising dependency on external integrators. Complex applications such as welding, advanced vision tasks, or precision machining require added hardware and skilled configuration. These factors increase total implementation cost and create barriers for budget-constrained businesses. Addressing this challenge requires user-friendly software, plug-and-play modules, and simplified deployment frameworks.
Safety Compliance and Performance Limitations in Heavy-Duty Tasks
Cobots are designed for safe, force-limited collaboration, but this restricts their speed, payload, and power in comparison to traditional industrial robots. For heavy-duty operations, performance trade-offs become evident, limiting cobot use in high-throughput environments. Companies must also comply with strict safety standards and conduct risk assessments before deployment, adding time and cost. These constraints slow adoption in industries requiring high speed, precision, or heavy load handling. Enhancing cobot strength while maintaining safety remains a key challenge for manufacturers.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds a 33% share of the Collaborative Robot market, driven by strong adoption across automotive, electronics, and metal fabrication industries. Manufacturers deploy cobots to enhance flexibility, address labor shortages, and support smart factory initiatives. The region benefits from advanced robotics ecosystems, strong investments in automation, and wide acceptance among SMEs. Growth also comes from expanding applications in logistics, healthcare, and research environments. Increasing integration of AI, vision systems, and predictive maintenance tools strengthens cobot performance, supporting wider deployment across high-mix, low-volume production settings.
Europe
Europe accounts for a 29% share, supported by strong industrial automation, high labor costs, and strict safety regulations that favor collaborative technologies. The region has a mature robotics market, with automotive and electronics sectors leading adoption of cobots for welding, assembly, and machine tending. Germany, France, and the Nordic countries invest heavily in Industry 4.0 upgrades that enhance precision and productivity. SMEs adopt cobots to improve operational efficiency and reduce dependency on skilled labor. Expanding use in packaging, food processing, and pharmaceuticals strengthens regional demand for flexible and safe automation.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific leads with a 31% share, driven by large-scale manufacturing across China, Japan, South Korea, and India. Strong expansion in automotive, consumer electronics, and semiconductor production fuels rapid cobot adoption for assembly, inspection, and material movement tasks. The region benefits from competitive production costs, strong robotics R&D activity, and government-backed automation programs. Manufacturers adopt cobots to address rising labor costs and improve productivity in high-volume operations. Growing integration of AI-enabled capabilities and advanced sensors further accelerates adoption across fast-growing industries.
Latin America
Latin America holds a 4% share, supported by increasing investment in automation within automotive, food processing, and metalworking industries. Brazil and Mexico lead cobot adoption as companies modernize production lines to improve efficiency and quality. Cobots gain traction among SMEs seeking cost-effective automation for repetitive and hazardous tasks. Rising interest in flexible assembly and packaging applications supports market growth. Although adoption remains at an early stage, supportive industrial policies and expanding manufacturing activity are expected to strengthen cobot penetration across the region.
Middle East & Africa
Middle East and Africa account for a 3% share, driven by growing automation needs in manufacturing, logistics, and industrial operations. The region sees rising adoption in automotive assembly, packaging, and metals processing as companies focus on productivity improvements. Countries in the Gulf Cooperation Council invest in robotics to support diversification beyond oil-driven industries. Cobots also gain traction in warehousing and healthcare applications due to their safety and flexibility. While adoption levels remain modest, expanding industrial infrastructure and interest in modern automation solutions support long-term market growth.
Market Segmentations:
By Payload
- Up to 5 kg
- 5-10 kg
- 10-25 kg
- More than 25 kg
By Application
- Material handling
- Assembling & dissembling
- Welding & soldering
- Others
By End Use Industry
- Automotive
- Electronics
- Metals & machining
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is shaped by major players such as Universal Robots, FANUC Corporation, ABB Ltd, KUKA AG, Yaskawa Electric Corporation, Doosan Robotics, Techman Robot Inc., AUBO Robotics, Rethink Robotics, and Nachi-Fujikoshi Corporation. These companies strengthen their market presence by expanding product portfolios, improving payload capacities, and integrating advanced AI-driven vision systems for higher precision and safety. Universal Robots continues to lead with a broad range of flexible cobots, while firms like Doosan Robotics and Techman Robot focus on intuitive interfaces and smart sensing technologies. Established robotics manufacturers such as FANUC and ABB invest heavily in collaborative automation as part of wider Industry 4.0 strategies. Strategic partnerships with system integrators, distributors, and software providers improve deployment speed and customization options for end users. Companies also prioritize global expansion through new manufacturing facilities, localized support centers, and industry-specific cobot solutions to meet growing demand across automotive, electronics, logistics, and metalworking sectors.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
- Universal Robots
- FANUC Corporation
- ABB Ltd
- KUKA AG
- Yaskawa Electric Corporation
- Doosan Robotics
- Techman Robot Inc.
- AUBO Robotics
- Rethink Robotics
- Nachi-Fujikoshi Corporation
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, Universal Robots introduced its fastest collaborative robot yet, the UR15, featuring motion speeds up to 5 m/s.
- In April 2025, FANUC Corporation announced that at Automate 2025 it will showcase its latest collaborative robots (cobots) featuring payloads up to 50 kg and long reach (~1,889 mm).
- In April 2025, Universal Robots announced that it and Mobile Industrial Robots would debut new AI-powered automation solutions across integrated workflows at Automate 2025.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Payload, Application, End Use Industry and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Demand for cobots will rise as industries expand flexible and smart automation.
- SMEs will accelerate adoption to improve productivity and reduce labor dependence.
- AI-driven vision systems will enhance cobot precision and enable complex task handling.
- Deployment in logistics and warehousing will grow due to e-commerce expansion.
- Healthcare and laboratory automation will adopt cobots for repetitive and delicate tasks.
- Higher payload and longer-reach cobots will support broader industrial applications.
- Easier programming and plug-and-play modules will reduce integration barriers.
- Safety-certified cobots will support closer human-robot collaboration on production floors.
- Regional manufacturing hubs will expand domestic cobot production and customization.
- Industry 4.0 and smart factory investments will drive continuous cobot integration.




