Market Overview
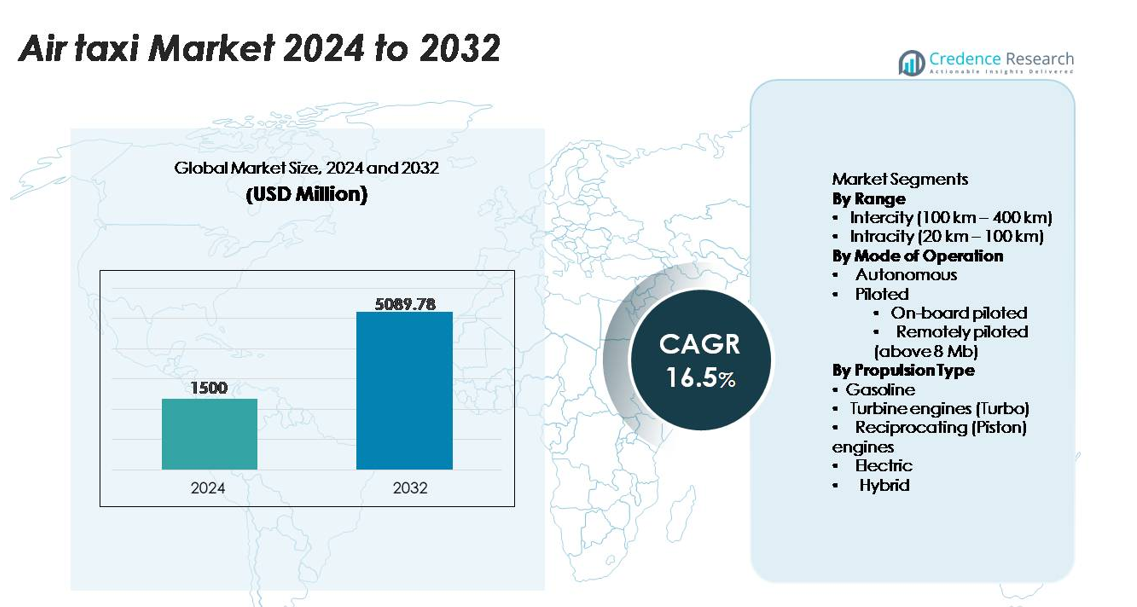
The global air taxi market was valued at USD 1,500 million in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 5,089.78 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 16.5% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Air Taxi Market Size 2024 |
USD 1,500 million |
| Air Taxi Market, CAGR |
16.5% |
| Air Taxi Market Size 2032 |
USD 5,089.78 million |
The air-taxi market is shaped by a mix of established aerospace leaders and high-growth eVTOL innovators, with companies such as Lilium N.V., Textron Aviation Inc., EHANG, Boeing, Beta Technologies, Volocopter GmbH, and Airbus advancing electric, hybrid, and autonomous flight platforms. These players compete by accelerating certification programs, scaling lightweight airframe production, and forming strategic alliances with airlines and vertiport developers. North America remains the leading region, holding approximately 38% of global market share, supported by strong regulatory progress, robust aerospace manufacturing capabilities, and early commercial trials. Europe and Asia-Pacific follow closely as emerging hubs for large-scale urban air-mobility deployment.
Market Insights
- The air-taxi market was valued at USD 1,500 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 5,089.78 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 16.5%.
- Strong market drivers include rapid adoption of electric and hybrid eVTOL platforms, expanding vertiport infrastructure, and growing demand for intracity mobility, with the Intracity segment holding the largest share due to high-frequency urban routes.
- Key trends center on autonomous-flight integration, AI-enabled navigation, lightweight composite airframes, and strategic partnerships between OEMs, airlines, and airport operators, accelerating commercial readiness.
- Competitive activity intensifies as leading players scale production, strengthen safety architectures, and pursue certification milestones, while restraints include infrastructure gaps, high development costs, and complex low-altitude airspace management.
- Regionally, North America leads with ~38% share, followed by Europe at ~27% and Asia-Pacific at ~24%, driven by regulatory readiness, UAM corridor development, and strong OEM presence, while Latin America and the Middle East & Africa expand gradually from smaller bases.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Range
The Intracity (20–100 km) segment holds the largest share of the air-taxi market as operators prioritize short-haul, high-frequency routes that support commuter mobility within dense urban environments. Intracity missions align well with current battery-electric range capabilities, allowing operators to maximize fleet utilization and minimize operational downtime. Strong government support for urban air mobility corridors and vertiport development also accelerates intracity deployment. Meanwhile, the Intercity (100–400 km) segment expands steadily as hybrid-electric and extended-range propulsion technologies mature, enabling regional connections between secondary cities and suburban clusters.
- For instance, Volocopter’s VoloCity engineered specifically for intracity deployment uses 18 independent electric motors, supports a total capacity for occupants (pilot and one passenger) and hand luggage of up to 200 kg (440 lbs), and is designed for an operational range of up to 35 km (22 miles) with a maximum airspeed of 110 km/h (68 mph).
By Mode of Operation
The Piloted segment currently dominates market share due to regulatory readiness, easier certification pathways, and operator preference for human oversight during early commercialization. Within this, On-board piloted operations lead because they reduce training complexity and align with existing aviation rules for air-taxi services. Remotely piloted (above 8 Mb) platforms are advancing through high-bandwidth command-and-control systems, but they require additional safety validation. Autonomous air taxis remain in development, with manufacturers integrating advanced sense-and-avoid, flight-management automation, and redundancy architectures to support future large-scale autonomous networks.
- For instance, Joby Aviation’s piloted S4 eVTOL prototype has accumulated over 30,000 propeller test hours across its electric propulsion system, reached a documented top speed of 332 km/h, and completed a 248 km point-to-point flight on a single charge during FAA-observed flight testing in 2023, demonstrating certified-grade performance for near-term piloted urban air-mobility operations.
By Propulsion Type
The Electric propulsion segment accounts for the dominant market share as manufacturers adopt battery-electric architectures to reduce emissions, simplify maintenance, and meet urban environmental mandates. Electric systems also support lower operating costs and quieter operations, critical for city-center vertiport approvals. Hybrid propulsion grows as a transitional solution for extended-range and intercity missions requiring higher endurance. Turbine and reciprocating piston engines retain niche roles in conventional air-taxi conversions, while gasoline propulsion remains limited due to fuel-cost volatility and rising sustainability targets across emerging air-mobility ecosystems.
Key Growth Drivers
Expansion of Urban Air Mobility (UAM) Infrastructure
Rapid investments in UAM corridors, vertiports, and integrated digital traffic-management systems significantly accelerate the adoption of air taxis across major metropolitan regions. Governments and private operators collaborate to deploy standardized takeoff and landing infrastructure that supports frequent, point-to-point aerial mobility, reducing pressure on congested road networks. Cities increasingly incorporate UAM into long-term transportation blueprints, prioritizing multimodal connectivity and sustainability. The integration of air taxis into smart-city ecosystems, supported by electrification roadmaps and urban planning frameworks, strengthens commercial viability. As more municipalities approve test beds and air routes, operators gain predictable environments for piloted services and future autonomous operations. This infrastructure-driven enablement ensures that air taxis evolve from experimental platforms to essential urban-mobility assets.
- For instance, Skyports Infrastructure and Groupe ADP’s full-scale UAM testbed at Pontoise–Cormeilles Airport in France features a 45-meter landing pad, dedicated charging infrastructure engineered for up to 150 kW output, and a digital FATO/approach system validated through more than 1,000 eVTOL test operations conducted with Volocopter’s VoloCity and other OEM demonstrators.
Advancements in Electric and Hybrid Propulsion Technologies
Breakthroughs in high-energy-density batteries, power electronics, and lightweight structural materials create major advantages for air-taxi platforms by enhancing range, reliability, and operational efficiency. Electric propulsion reduces mechanical complexity, enabling lower maintenance requirements and improved uptime for fleet operators. Hybrid-electric architectures extend mission profiles for intercity travel without compromising environmental benefits, while next-generation thermal management systems improve performance during continuous high-cycle operations. Manufacturers increasingly integrate modular propulsion units, improving scalability and certification processes. These technological improvements also enable quieter operations crucial for community acceptance and deployment near dense urban centers. As propulsion systems achieve higher endurance and stricter safety thresholds, commercial operators gain confidence to expand services, reinforcing long-term market growth.
- For instance, Joby Aviation’s eVTOL uses commercially available lithium-nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC 811) pouch cells delivering 288 Wh/kg cell-level specific energy (235 Wh/kg at the pack level), enabling a record demonstration flight covering 241 km (150 miles) on a single charge.
Regulatory Progress and Certification Pathways
Regulatory authorities accelerate frameworks for certifying electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft, airworthiness standards, and operational procedures for emerging air-taxi fleets. Clearer guidelines for piloted operations, redundancy architectures, and noise-compliance parameters enable manufacturers to advance toward type certification with greater predictability. The development of standardized pilot training protocols and maintenance programs further supports early-stage deployments. Air-navigation service providers also progress toward digital air-traffic management systems capable of handling high-density, low-altitude operations. These regulatory advancements reduce entry barriers, attract new investors, and provide a foundation for scaling regional and intracity services. As certification pathways mature globally, cross-border harmonization ensures consistent operational rules, accelerating the transition from prototype demonstrations to commercial operations.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Emergence of Passenger-Centric eVTOL Design and Fleet Personalization
Manufacturers shift focus toward cabin comfort, noise reduction, and ergonomic layouts as air taxis transition from experimental prototypes to customer-facing transportation modes. Passenger-centric designs featuring panoramic windows, vibration isolation, adaptive seating, and digital booking interfaces enhance user experience and increase adoption among premium commuters. Fleet personalization becomes a major opportunity, with operators offering differentiated service tiers, including business-class configurations, shared-ride models, and tourism-focused aerial experiences. Advanced digital interfaces integrate real-time flight updates, route optimization, and multimodal connections, enabling seamless mobility. These refinements align air taxis with evolving consumer expectations, positioning eVTOL platforms as viable alternatives to helicopters and high-cost ground mobility services.
- For instance, Lilium’s 7-seat Jet features a 1.6-meter cabin width, customizable club-seating configurations, and noise levels measured at below 60 dBA during takeoff at 100 meters verified in 2023 acoustic-validation tests.
Integration of AI, Autonomy, and Predictive Maintenance Ecosystems
AI-enabled flight-control algorithms, real-time obstacle detection, and autonomous navigation systems unlock large-scale operational efficiency for future air-taxi fleets. Operators leverage predictive maintenance tools to monitor structural health, battery cycles, propulsion performance, and critical sensor functions, enabling optimized maintenance windows and reducing unplanned downtime. Digital twins simulate aircraft behavior under multiple operational conditions, supporting improved reliability and safety validation. These technologies also lay the foundation for autonomous or remotely piloted operations, significantly lowering pilot-related cost structures. As autonomy matures, operators gain opportunities to expand into high-frequency urban shuttle networks, improving scalability across cities and regional corridors.
- For instance, Wisk Aero’s Generation-6 autonomous eVTOL uses six independent flight computers executing continuous cross-checking algorithms while processing over 1,000 sensor inputs per second to ensure fault-tolerant flight control performance validated during Boeing-supported autonomy trials in 2023.
Key Challenges
Infrastructure Limitations and Airspace Integration Complexity
Despite rapid advancements, large-scale air-taxi deployment faces persistent challenges related to vertiport availability, zoning approvals, and integration with existing airspace structures. Urban centers struggle to allocate suitable rooftop or ground-based sites while meeting noise, safety, and energy-supply requirements. Coordinating low-altitude flight corridors with helicopter, drone, and general aviation operations adds further complexity. Air-traffic management systems must evolve to support dense, simultaneous movements of piloted and eventually autonomous eVTOLs. These gaps delay network expansion and elevate operational uncertainty for early entrants. Without synchronized infrastructure and airspace modernization, large-scale commercial air-taxi adoption faces structural bottlenecks.
High Operational Costs and Certification Burdens
Air-taxi manufacturers and fleet operators contend with high costs linked to R&D, battery systems, composite materials, pilot training, and insurance—factors that challenge initial profitability. Certification processes require extensive testing across propulsion reliability, crashworthiness, and flight-software validation, increasing development timelines. Additionally, evolving regulatory expectations force companies to continuously upgrade safety instruments and redundancy systems, adding cost pressure. Operators must also balance charging infrastructure investments, fleet management technologies, and maintenance capabilities. These cumulative financial and technical constraints slow large-scale commercialization and limit early adoption outside premium routes.
Regional Analysis
North America
North America holds the largest share of the global air-taxi market at approximately 38%, driven by strong FEMA, NASA, and FAA-backed initiatives supporting eVTOL certification and early deployment. Major operators conduct high-frequency demonstration flights across the U.S., supported by robust venture funding and mature aerospace manufacturing clusters. Numerous cities, including Los Angeles, New York, and Dallas, advance vertiport planning, enabling early commercial rollouts of piloted and future autonomous services. Strong governmental emphasis on advanced air mobility corridors and urban congestion reduction further accelerates U.S. market leadership, positioning the region as the global test bed for full-scale urban air mobility networks.
Europe
Europe accounts for around 27% of the global air-taxi market, supported by progressive EASA regulatory pathways, national UAM strategies, and strong collaborations among OEMs, airports, and mobility operators. Germany, France, and the U.K. lead deployment, with cities integrating air taxis into climate-neutral mobility plans. European manufacturers benefit from solid engineering expertise and strong public-sector funding for electric aviation. Demonstration routes planned for Paris 2024 and emerging vertiport projects in the U.K. and Scandinavia boost momentum. The region’s emphasis on low-noise, zero-emission mobility strengthens demand for electric propulsion platforms and high-density intracity flight networks.
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific captures approximately 24% of the market, fueled by rapid urbanization, megacity congestion, and aggressive government investment in advanced air mobility ecosystems. China, Japan, Singapore, and South Korea lead certification trials and commercial pilot programs, particularly for intracity and short-intercity routes. Regional OEMs accelerate development of electric and hybrid eVTOLs tailored to dense urban clusters and high-frequency shuttles. Policymakers in Japan and South Korea fast-track flight-permission frameworks, while China expands air-routes for autonomous demonstration flights. Strong demand for premium mobility, infrastructure modernization, and tourism-based aerial transport further strengthens APAC’s high-growth trajectory.
Latin America
Latin America represents about 6% of the global air-taxi market, supported primarily by early adoption in Brazil, Mexico, and Colombia. Major metropolitan areas such as São Paulo with its extensive helicopter culture serve as natural entry points for eVTOL-based air taxis. Regional demand centers on reducing traffic congestion, enhancing airport-city connectivity, and expanding aerial mobility for business travelers. Partnerships between regional aviation authorities and global eVTOL manufacturers accelerate vertiport planning and pilot certifications. However, infrastructure gaps and regulatory constraints slow broader adoption, although opportunities remain strong in tourism, high-density corridors, and premium executive transport.
Middle East & Africa
The Middle East & Africa region accounts for approximately 5% market share, driven mainly by innovation hubs in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Israel. Dubai leads regional deployment with dedicated UAM corridors and early commercial route planning under supportive aviation authorities. Saudi Arabia’s smart-city projects, including NEOM, integrate air taxis into long-term mobility strategies with large-scale infrastructure investments. While Africa remains nascent, select countries explore air taxis for medical logistics and remote connectivity. The region’s strong capital investment capacity and ambitious smart-infrastructure goals position it as a future growth hotspot once regulatory and operational frameworks fully mature.
Market Segmentations:
By Range
- Intercity (100 km – 400 km)
- Intracity (20 km – 100 km)
By Mode of Operation
- Autonomous
- Piloted
- On-board piloted
- Remotely piloted (above 8 Mb)
By Propulsion Type
- Gasoline
- Turbine engines (Turbo)
- Reciprocating (Piston) engines
- Electric
- Hybrid
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- U.K.
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- South-east Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the air-taxi market is shaped by rapid technological innovation, accelerated certification timelines, and increasing collaboration between aerospace manufacturers, mobility operators, and infrastructure developers. Leading eVTOL companies advance electric and hybrid propulsion platforms optimized for intracity and short-intercity missions, supported by significant venture funding and strategic partnerships with major airlines. Firms prioritize noise reduction, redundant flight-control systems, lightweight composite structures, and scalable production lines to meet safety and performance requirements. Concurrently, operators form alliances with vertiport developers and urban authorities to secure early route access and operational readiness. Traditional aerospace players strengthen their presence through investments in digital twins, autonomous flight software, and high-reliability components, intensifying competitive pressure. As regulatory agencies streamline type certification and operational approvals, competition increasingly shifts toward fleet commercialization, pilot training capabilities, maintenance ecosystems, and total operating cost efficiency. Overall, the market remains dynamic, with early movers gaining strategic advantage through integrated technology and infrastructure partnerships.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Player Analysis
Recent Developments
- In June 2025, Boeing (via its subsidiary Wisk Aero)Wisk Aero acquired air-space-integration firm SkyGrid as part of its plan to advance its Generation-6 autonomous eVTOL aircraft and U.S. market service launch.
- In October 2025 the company EHANG unveiled its new VT35 autonomous eVTOL aircraft capable of nearly 125 miles on a single charge (two-seat pilotless model).
- In October 2024, Textron Aviation Inc its subsidiary Textron eAviation announced full-scale flight-testing for its “Nexus” eVTOL demonstrator at Salina Regional Airport
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Range, Mode of operation, Propulsion type and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Air taxis will transition from pilot-led operations to increasingly autonomous flight modes as regulatory frameworks mature.
- Vertiport networks will expand across major cities, enabling higher-frequency intracity and short regional routes.
- Advances in battery density and hybrid systems will extend operational range and reduce turnaround times.
- Operators will adopt predictive maintenance and digital-twin technologies to optimize fleet reliability.
- Noise-reduction engineering will improve community acceptance and support more city-center deployments.
- Strategic alliances between OEMs, airlines, and mobility platforms will accelerate large-scale commercialization.
- Standardized global certification pathways will reduce entry barriers and support cross-border air-taxi operations.
- Manufacturing capacity for eVTOL aircraft will scale significantly through automation and modular assembly.
- Consumer adoption will rise as air-taxi services integrate into multimodal transportation systems.
- Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East will drive long-term expansion with smart-city investments.




