| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Indonesia Diabetes Drugs Market Size 2023 |
USD 482.65 Million |
| Indonesia Diabetes Drugs Market, CAGR |
2.62% |
| Indonesia Diabetes Drugs Market Size 2032 |
USD 631.76 Million |
Market Overview
Indonesia Diabetes Drugs Market size was valued at USD 482.65 million in 2023 and is anticipated to reach USD 631.76 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 2.62% during the forecast period (2023-2032).
The Indonesia Diabetes Drugs market is driven by a growing diabetic population, rising awareness of diabetes management, and advancements in drug formulations. As lifestyle-related diseases become more prevalent, the demand for effective diabetes medications increases, leading to a surge in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes cases. Additionally, improved healthcare infrastructure and access to treatment options contribute to market expansion. Increasing government initiatives and programs focused on diabetes prevention and management also play a pivotal role in driving the market. Moreover, the introduction of new and innovative diabetes medications, including injectable therapies and oral drugs, is enhancing treatment options and improving patient outcomes. Market players are capitalizing on these opportunities, developing drugs with better efficacy and fewer side effects. Trends such as personalized medicine, the growing emphasis on early diagnosis, and the rise of telemedicine in diabetes care are further shaping the market’s growth trajectory.
Geographically, the Indonesian diabetes drugs market is primarily driven by urban centers in Java, where healthcare access and awareness are more prominent. The western regions, including Jakarta and Surabaya, dominate the market due to their high population density and better healthcare infrastructure. Other regions like Sumatra, Kalimantan, and Sulawesi are witnessing steady growth as healthcare improves and awareness increases. Key players in the Indonesia diabetes drugs market include global pharmaceutical giants such as Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Merck & Co., Sanofi, and AstraZeneca. These companies lead the market with their diverse range of diabetes treatments, including insulin, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors. Local players and regional distributors are also strengthening their position by expanding their product offerings and enhancing distribution networks. These key players are increasingly focusing on expanding their presence in both urban and rural areas to cater to the growing demand for diabetes management.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Indonesia diabetes drugs market was valued at USD 482.65 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 631.76 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 2.62% during the forecast period.
- The growing prevalence of diabetes, particularly type 2, due to urbanization, changing diets, and sedentary lifestyles, is a key driver of the market.
- Advancements in drug formulations, including GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors, and newer insulin therapies, are enhancing treatment options and driving market growth.
- The trend toward personalized medicine and digital health solutions, such as mobile apps and wearables, is gaining momentum in diabetes management.
- The market faces challenges such as limited access to healthcare in rural areas and the high cost of advanced diabetes treatments.
- Leading competitors like Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Merck & Co., and Sanofi dominate the market with their innovative drug portfolios.
- Regional growth is strongest in urban centers in Java, while other regions like Sumatra and Kalimantan show steady growth.
Report Scope
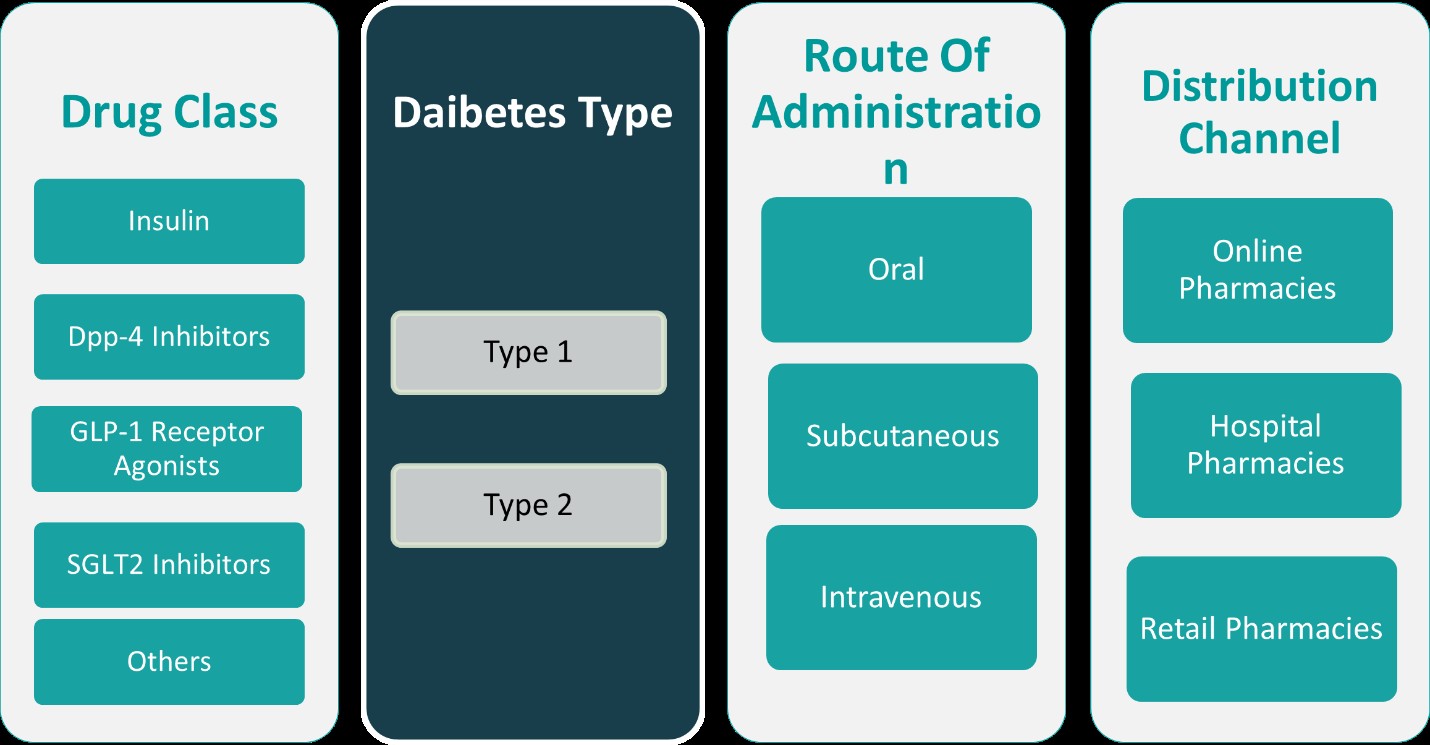
This report segments the Indonesia Diabetes Drugs Market as follows:
Market Drivers
Growing Prevalence of Diabetes
The increasing prevalence of diabetes in Indonesia is one of the most significant drivers of the diabetes drugs market. For instance, the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) reported that Indonesia ranks among the top ten countries globally for diabetes prevalence, with over 19 million adults affected as of 2021. The rapid urbanization, changing dietary habits, sedentary lifestyles, and an aging population contribute to the growing incidence of type 2 diabetes. As more individuals are diagnosed with the condition, the demand for diabetes medications, including oral drugs and insulin therapies, rises. Early diagnosis and effective management of diabetes are crucial, further amplifying the need for accessible and advanced treatment options.
Advancements in Diabetes Medications
The continuous advancements in diabetes drugs have spurred market growth in Indonesia. For instance, recent innovations include the approval of oral GLP-1 receptor agonists by the Indonesian Food and Drug Authority, offering patients a non-invasive alternative to injectable therapies. These drugs have shown to improve blood sugar control, reduce complications, and enhance patients’ quality of life. As the pharmaceutical industry invests in research and development (R&D) for more effective therapies, the availability of cutting-edge diabetes drugs has bolstered the market. The introduction of combination therapies, which target multiple mechanisms in the body, is also driving market expansion, providing more comprehensive treatment solutions for patients.
Government Initiatives and Healthcare Improvements
Government policies and initiatives aimed at improving healthcare access and managing chronic diseases, such as diabetes, are vital drivers of the diabetes drugs market in Indonesia. The Indonesian government has been increasingly focused on enhancing healthcare infrastructure, ensuring the availability of medicines, and expanding health insurance coverage. Public awareness campaigns about diabetes prevention and management have also gained momentum in recent years. Furthermore, efforts to increase healthcare accessibility, particularly in rural and underserved areas, ensure that more patients receive timely diagnosis and treatment. As healthcare access improves, the demand for diabetes drugs continues to grow, supporting the market’s positive outlook.
Growing Awareness and Shifting Patient Demographics
Increased awareness of diabetes and its management is playing a crucial role in expanding the market. Over the past few years, there has been a shift in how the Indonesian public views diabetes, with a growing understanding of its risks and the importance of managing it effectively. Public health campaigns, diabetes education programs, and the role of healthcare providers in educating patients about the importance of medication adherence have contributed to a more informed patient population. Additionally, the demographic shift in Indonesia, with a growing middle class and an aging population, has led to a larger segment of the population seeking diabetes treatment. This shift has created an opportunity for both domestic and international pharmaceutical companies to introduce their products to a wider audience, thus accelerating market growth.
Market Trends
Emergence of Personalized Medicine
A prominent trend shaping the Indonesia diabetes drugs market is the growing focus on personalized medicine. For instance, a study by the Indonesian Diabetes Association emphasized the importance of tailoring treatments based on genetic and lifestyle factors, which has led to the adoption of genomic profiling in select healthcare facilities. This approach enhances the efficacy of treatments, minimizes side effects, and promotes better long-term management of the disease. Personalized medicine is transforming diabetes care by offering patients drugs that are best suited to their unique health profiles, thereby improving patient outcomes and adherence to treatment regimens.
Integration of Digital Health Technologies
The integration of digital health technologies is another key trend in Indonesia’s diabetes drugs market. For instance, the Indonesian Ministry of Health’s “Satu Sehat” platform enables real-time monitoring of blood glucose levels and medication adherence through mobile health apps and wearable devices. With the support of digital health tools, patients and healthcare providers can make more informed decisions about treatment, leading to better disease management. Moreover, telemedicine has expanded access to diabetes care, particularly in remote areas where healthcare resources are limited. The convergence of digital health with diabetes drug therapies is streamlining patient care and improving overall treatment outcomes.
Shift Towards Injectable and Combination Therapies
Another emerging trend in the diabetes drugs market in Indonesia is the shift towards injectable therapies and combination treatments. Injectable insulin therapies, as well as newer classes of injectable drugs like GLP-1 receptor agonists, are gaining popularity due to their effectiveness in controlling blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of complications. Combination therapies, which include both oral medications and injectables, offer a more holistic approach to diabetes management. These therapies allow for better blood glucose control by targeting multiple mechanisms simultaneously, leading to more comprehensive treatment plans. The trend towards injectable and combination therapies reflects the growing demand for more advanced and effective treatments that offer convenience and improved patient compliance.
Increasing Focus on Preventive Care
The growing emphasis on preventive care is another key trend in Indonesia’s diabetes drugs market. As the prevalence of type 2 diabetes continues to rise, there is an increasing focus on preventing the onset of the disease, especially in high-risk populations. Preventive measures, including lifestyle modifications, early screenings, and the use of medications to prevent diabetes in prediabetic patients, are becoming more common. Drugs such as metformin, traditionally used for managing diabetes, are also being prescribed for preventive purposes in those at high risk. By addressing diabetes at an earlier stage, healthcare providers are aiming to reduce the overall burden of the disease and prevent complications, which in turn drives demand for medications and management strategies.
Market Challenges Analysis
Limited Access to Healthcare in Rural Areas
One of the key challenges facing the Indonesia diabetes drugs market is the limited access to healthcare, particularly in rural and remote areas. For instance, a report by the Indonesian Basic Health Research (RISKESDAS) revealed that only 30% of rural diabetes patients have access to essential medications, compared to 70% in urban areas. This geographic disparity affects the timely diagnosis and treatment of diabetes, leaving a significant portion of the population without proper care. As a result, patients in rural areas may delay seeking treatment or may not have access to the latest diabetes drugs. The lack of healthcare resources in these regions hinders market growth, as effective disease management requires consistent access to medications and healthcare professionals.
High Drug Costs and Affordability Issues
Another significant challenge is the high cost of diabetes medications, which can limit accessibility for a large segment of the Indonesian population. While the government has taken steps to make healthcare more affordable, the cost of certain advanced diabetes treatments, particularly newer drugs and insulin formulations, remains a barrier for many individuals. For patients without adequate insurance coverage, the cost of ongoing diabetes management can be prohibitive. This affordability issue affects both individuals and healthcare systems, slowing the adoption of newer, more effective treatments. Addressing the pricing of diabetes drugs and improving access to affordable healthcare are critical to overcoming this challenge and ensuring broader access to necessary treatments across all socio-economic groups.
Market Opportunities
The Indonesia diabetes drugs market presents several growth opportunities driven by the increasing prevalence of diabetes and the rising demand for effective treatment options. As the number of diabetic patients continues to grow, there is a significant opportunity for pharmaceutical companies to introduce innovative medications that cater to the specific needs of the Indonesian population. This includes expanding the availability of advanced oral and injectable therapies, particularly for type 2 diabetes, where more effective options are being developed. Additionally, as awareness of diabetes management and prevention increases, there is a growing market for drugs that target the early stages of the disease, such as metformin and GLP-1 receptor agonists. This presents an opportunity to target prediabetic populations and develop preventative treatments, which can reduce the overall healthcare burden and promote early intervention strategies.
Moreover, the Indonesian government’s initiatives to improve healthcare access and expand insurance coverage create further market potential. As healthcare infrastructure continues to develop, particularly in underserved rural areas, pharmaceutical companies can expand their reach and ensure that essential diabetes medications are accessible to a broader demographic. Additionally, the integration of digital health technologies into diabetes care provides an opportunity for innovative solutions that combine medication with real-time monitoring and telemedicine. This convergence of diabetes management drugs and digital tools is creating a more efficient and personalized approach to patient care, which could lead to improved treatment adherence and better health outcomes. Companies that invest in both drug development and digital health solutions are likely to see significant opportunities for growth in the rapidly evolving Indonesian market.
Market Segmentation Analysis:
By Drug Class:
The Indonesia diabetes drugs market is segmented based on various drug classes, with insulin, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors, and other categories playing significant roles. Insulin remains one of the most commonly used drugs, particularly for type 1 diabetes patients, who rely on insulin for blood sugar regulation. The demand for insulin continues to grow, driven by the increasing prevalence of diabetes. DPP-4 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists are gaining traction, especially for type 2 diabetes patients. DPP-4 inhibitors work by enhancing insulin secretion and reducing glucagon levels, while GLP-1 receptor agonists improve glucose control and promote weight loss, making them increasingly popular among patients with type 2 diabetes. SGLT2 inhibitors are also emerging as an essential class of drugs due to their ability to reduce blood sugar levels and prevent complications like kidney disease. These drug classes cater to diverse patient needs, making them crucial segments in the market, with future growth expected in line with expanding treatment options.
By Diabetes Types:
The market segmentation based on diabetes types highlights the distinct needs of patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, alongside emerging categories such as diabetes type 3, type 4, and type 5. Type 1 diabetes, typically diagnosed in childhood or early adulthood, requires insulin therapy for life. This segment will continue to drive demand for insulin-based products. Type 2 diabetes, which is more prevalent and often linked to lifestyle factors, contributes significantly to the market, with treatments focused on oral medications, GLP-1 receptor agonists, DPP-4 inhibitors, and SGLT2 inhibitors. Emerging types such as diabetes type 3, which is associated with Alzheimer’s disease, and type 4 and type 5, often linked to specific genetic or lifestyle factors, represent growing segments that are gaining attention from pharmaceutical companies. As awareness of these types increases, new drugs may be developed to cater to their unique characteristics. This evolving landscape provides substantial growth potential for diabetes drug developers targeting diverse patient populations.
Segments:
Based on Drug Class:
- Insulin
- DPP-4 Inhibitors
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
- SGLT2 Inhibitors
- Others
Based on Diabetes Types:
- Type 1
- Type 2
- Diabetes Type 3
- Diabetes Type 4
- Diabetes Type 5
Based on Route of Administration:
- Oral
- Subcutaneous
- Intravenous
- Route of Administration 4
- Route of Administration 5
Based on Technology:
- Technology 1
- Technology 2
- Technology 3
Based on Distribution Channel:
- Online Pharmacies
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Distribution Channel 4
- Distribution Channel 5
Based on the Geography:
- Java
- Sumatra
- Kalimantan
- Sulawesi
Regional Analysis
Java
Java, the most populous and urbanized region, holds the largest market share, accounting for approximately 50% of the total diabetes drugs market. This dominance is driven by its high population density, significant urban centers like Jakarta, Surabaya, and Bandung, and better access to healthcare services. Java’s market is characterized by a high demand for both insulin therapies for type 1 diabetes and oral medications such as DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors for type 2 diabetes. The region’s urbanization, changing lifestyles, and higher incidence of diabetes contribute to the continued growth of diabetes drug sales.
Sumatra
Sumatra holds around 20% of the market share, driven by cities like Medan and Padang, which are emerging as regional healthcare hubs. While healthcare access in rural areas of Sumatra remains a challenge, the increasing awareness of diabetes management and improvements in local healthcare infrastructure are fostering market growth. Insulin-based therapies remain prevalent in Sumatra, particularly for type 1 diabetes patients, while the demand for oral drugs like DPP-4 inhibitors and SGLT2 inhibitors for type 2 diabetes management is also increasing. As more patients seek advanced therapies, the region is expected to see steady growth in the diabetes drugs market over the next few years.
Kalimantan
Kalimantan accounts for approximately 15% of the diabetes drugs market share. Although the region is less densely populated compared to Java and Sumatra, Kalimantan is witnessing growing demand for diabetes medications as diabetes awareness increases. The expanding healthcare infrastructure, driven by both government and private sector investments, is contributing to the market’s expansion. Insulin therapies are in demand for type 1 diabetes management, while oral medications, including DPP-4 inhibitors, are increasingly being prescribed for type 2 diabetes patients. As urbanization continues and access to diabetes care improves, Kalimantan’s market share is expected to grow steadily.
Sulawesi
Sulawesi, with a market share of around 15%, is the smallest of the four regions but is experiencing gradual market growth. Key cities like Makassar are seeing an increase in the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes, with growing demand for insulin and oral diabetes medications. The region’s market is still developing, but improvements in healthcare infrastructure and awareness programs are gradually driving the adoption of more advanced therapies such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors. As healthcare services expand and more patients seek diabetes management, Sulawesi’s market share is expected to increase over the coming years.
Key Player Analysis
- Novo Nordisk A/S
- Sanofi
- Merck & Co., Inc
- Eli Lilly and Company
- AstraZeneca
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited
- Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
- Novartis AG
- Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.
- Bayer AG
- Pfizer
- Janssen Pharmaceuticals
- Company 13
- Company 14
Competitive Analysis
The Indonesia diabetes drugs market is highly competitive, with several global pharmaceutical giants dominating the space. Leading players include Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Merck & Co., Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Johnson & Johnson, Bayer, Pfizer, and Janssen Pharmaceuticals. These companies offer a diverse range of diabetes treatments, such as insulin, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors, catering to both type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients. The market is primarily driven by global companies that lead in the development and distribution of innovative diabetes therapies, including insulin, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors. These companies focus on providing a diverse range of treatments for type 1 and type 2 diabetes, helping to address the growing demand for advanced and effective therapies.
Multinational companies dominate the market through their established product portfolios, large-scale production capabilities, and strong distribution networks. Local players, however, are gaining market share by offering cost-effective alternatives and expanding their reach into both urban and rural areas. In addition, the competition is intensified by ongoing innovations in drug formulations, such as combination therapies, that provide patients with more comprehensive treatment options. Price sensitivity in certain regions, particularly in rural areas, has led to the emergence of generic products and biosimilars, further increasing market competition. The increasing awareness of diabetes management and improvements in healthcare infrastructure across the country create additional opportunities for both established and emerging players to expand their market presence.
Recent Developments
- In March 2025, Novo Nordisk signed a deal worth up to $2 billion for the rights to UBT251, a new obesity and diabetes drug developed by United BioTechnology. The drug combines GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon to manage blood sugar and reduce hunger.
- In February 2025, Sanofi received FDA approval for MERILOG, the first rapid-acting insulin aspart biosimilar, to improve glycemic control in adults and pediatric patients with diabetes.
- In December 2024, JD Health began offering Merck’s GLUCOPHAGE XR (Reduce Mass) online in China, enhancing access to metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets for type 2 diabetes patients.
- In December 2024, Torrent Pharma acquired three diabetes brands from Boehringer Ingelheim, including those with Empagliflozin, to strengthen its anti-diabetes portfolio
- In November 2024, AstraZeneca presented promising early data for its obesity pipeline, including AZD5004, an oral GLP-1 receptor blocker, at Obesity Week 2024.
Market Concentration & Characteristics
The Indonesia diabetes drugs market exhibits moderate concentration, with a few multinational pharmaceutical companies holding significant market share. These global players dominate the market through their established brands, extensive distribution networks, and broad product portfolios that include insulin, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors. However, local players are steadily increasing their presence, offering more affordable alternatives and catering to specific regional needs. The market is characterized by a high degree of innovation, with continuous advancements in drug formulations, including combination therapies, to improve treatment outcomes for diabetes patients. Additionally, the rising demand for personalized treatment options, coupled with the integration of digital health solutions, has added a new dimension to the competitive landscape. While large players lead the market, local and regional competitors are gaining traction by focusing on price-sensitive segments and expanding their reach in both urban and rural areas of Indonesia.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Drug Class, Diabetes Types, Route of Administration, Technology, Distribution Channel and Geography. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- The Indonesia diabetes drugs market is expected to grow steadily, driven by the increasing prevalence of diabetes, particularly type 2.
- There will be a rising demand for advanced diabetes treatments, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors, and combination therapies.
- Growing awareness of diabetes management and prevention will contribute to higher adoption of medications across various regions.
- The government’s focus on expanding healthcare access and improving insurance coverage will enhance medication availability.
- Digital health technologies, including mobile apps and wearables, will become more integrated into diabetes care, improving treatment adherence.
- Local pharmaceutical companies will expand their presence by offering affordable alternatives, addressing the price-sensitive market.
- Market competition will intensify with the entry of biosimilars and generic drugs, providing more cost-effective options.
- As healthcare infrastructure improves in rural areas, demand for diabetes medications is expected to rise in underserved regions.
- The shift toward personalized medicine and targeted treatments will lead to more effective diabetes management strategies.
- The market will see an increased focus on preventive care, with drugs aimed at managing prediabetes and delaying the onset of type 2 diabetes.




