Market Overview
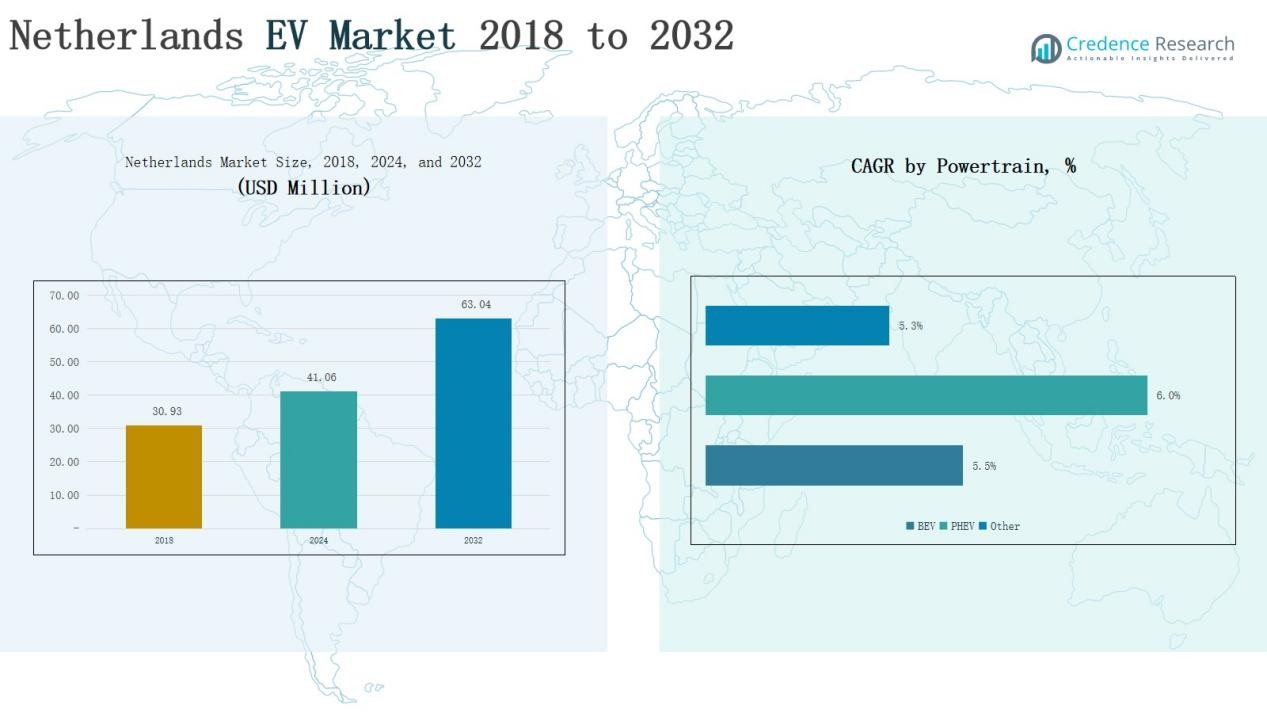
Netherlands Electric Vehicle (EV) Market size was valued at USD 17.99 million in 2018 to USD 25.08 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 41.17 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 6.09% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2032 |
| Netherlands EV Market Size 2024 |
USD 25.08 Million |
| Netherlands EV Market, CAGR |
6.09% |
| Netherlands EV Market Size 2032 |
USD 41.17 Million |
The Netherlands EV Market is shaped by strong competition among leading automakers, each driving adoption through innovation, affordability, and sustainability. Volkswagen, BMW AG, Mercedes-Benz, Tesla, Volvo, Audi, Skoda, Dott, and Geely Holding dominate the landscape with diversified product portfolios and strategic investments in charging infrastructure. Tesla leads the premium BEV category with advanced technology and an extensive supercharger network, while Volkswagen and Volvo drive mass-market penetration with affordable, reliable models. Luxury brands such as BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Audi reinforce their presence through performance-focused EVs, while Geely Holding and Skoda expand accessibility with cost-efficient offerings. Local operator Dott complements adoption by advancing micro-mobility solutions. Regionally, Eastern Netherlands commanded the largest share at 45% in 2024, supported by dense urbanization, advanced charging networks, and strong policy frameworks that continue to accelerate consumer and corporate adoption.
Access crucial information at unmatched prices!
Request your sample report today & start making informed decisions powered by Credence Research Inc.!
Download Sample
Market Insights
- The Netherlands EV Market grew from USD 17.99 million in 2018 to USD 25.08 million in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 41.17 million by 2032 at a CAGR of 6.09%.
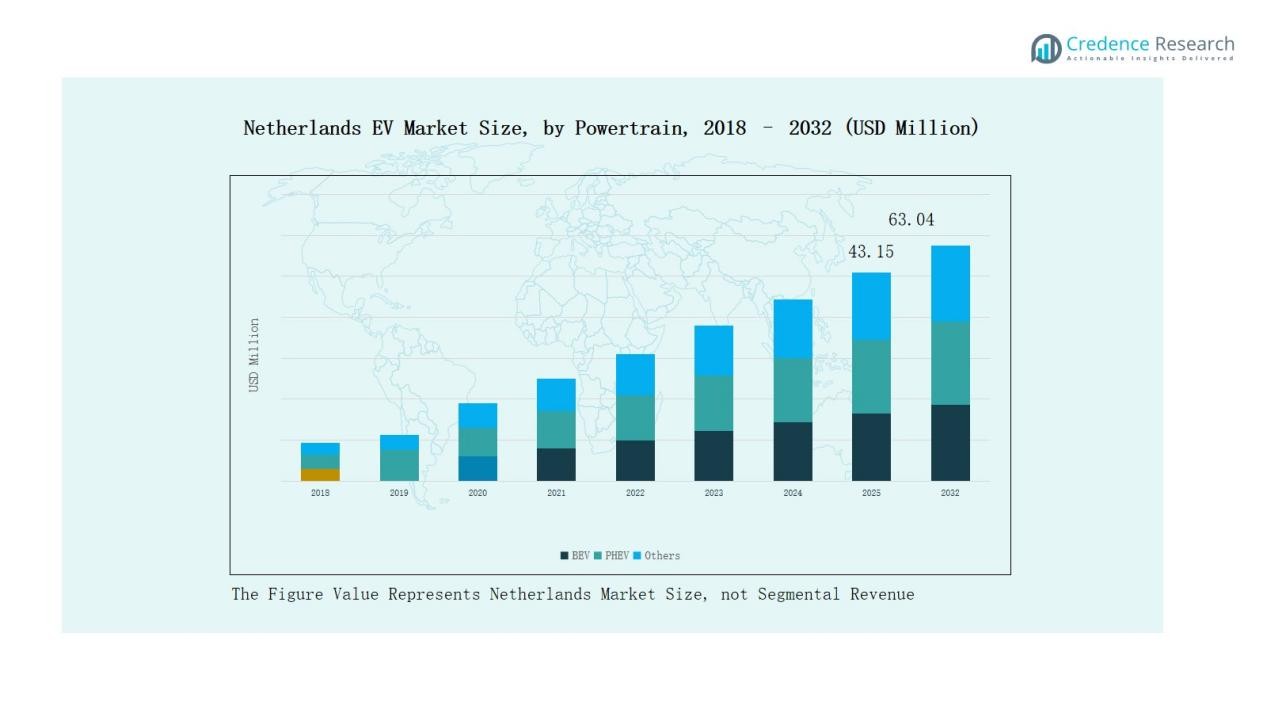
- Battery Electric Vehicles held the largest share with 68% in 2024, while Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles captured 24% and other powertrain types accounted for 8%.
- Private buyers dominated end-user adoption with 71% share in 2024, supported by incentives and tax benefits, while corporate buyers contributed 29% through fleet electrification programs.
- Eastern Netherlands led regionally with 45% share in 2024, followed by Western Netherlands at 32%, Northern Netherlands at 13%, and Southern Netherlands at 10%.
- Key players include Volkswagen, BMW AG, Mercedes-Benz, Tesla, Volvo, Audi, Skoda, Dott, and Geely Holding, each competing through innovation, affordability, and charging infrastructure expansion.
Market Segment Insights
By Powertrain
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) dominate the Netherlands EV Market, holding 68% share in 2024. Growth is driven by strong government incentives, zero-emission targets, and an extensive charging network supporting nationwide adoption. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) accounted for 24% share, supported by buyers seeking range flexibility for both short commutes and longer trips. The remaining 8% share comes from other powertrain options, including fuel cell EVs and hybrid technologies, appealing to niche buyers focused on alternative solutions.
- For instance, BYD launched its Dolphin hatchback in the Dutch market, expanding its affordable BEV portfolio and meeting growing demand from first-time EV buyers.
By End User
Private buyers represent the dominant segment, capturing 71% share in 2024. Their uptake is fueled by financial incentives, tax exemptions, and a growing preference for sustainable personal mobility. Corporate buyers hold 29% share, with demand led by fleet electrification programs, sustainability commitments, and cost-efficient operations. The corporate segment continues to expand steadily as businesses align with national emission-reduction policies and low-emission zone requirements in Dutch cities.
- For instance, in the Netherlands, 48% of new car registrations in 2024 were attributed to businesses, with 55.9% of company-cars being rechargeable (BEVs or PHEVs).
Key Growth Drivers
Strong Government Incentives and Regulations
Government policies remain a major driver of EV adoption in the Netherlands. Tax benefits, registration fee exemptions, and subsidies for EV purchases encourage private and corporate buyers. The Dutch government also enforces strict emission standards and plans to phase out fossil fuel vehicles by 2035. These regulatory frameworks create a strong push toward electric mobility. Together, financial incentives and legislative measures provide stability for automakers and consumers, reinforcing BEV adoption as the dominant powertrain segment.
- For instance, Tesla’s Model 3 benefitted from the Dutch subsidy scheme launched in July 2020, making new BEVs priced between €12,000-€45,000 eligible for a €4,000 rebate.
Expanding Charging Infrastructure
The Netherlands leads Europe in charging station density, significantly boosting EV adoption. The country has invested heavily in public and private charging networks, ensuring easy access for urban and rural users. Fast-charging corridors across highways reduce range anxiety and support long-distance travel. Home and workplace charging initiatives further enhance convenience for private and fleet buyers. This robust infrastructure provides a foundation for sustained EV penetration and reinforces consumer confidence, making the transition to electric mobility more practical and attractive.
- For instance, Shell Recharge announced it had installed over 500 public fast-charging points across the Netherlands, expanding its nationwide network to support highway and city driving.
Rising Consumer Preference for Sustainability
Environmental awareness among Dutch consumers drives demand for zero-emission vehicles. Growing concerns about climate change and air pollution are shifting preferences from traditional cars to electric alternatives. Younger demographics, in particular, view EVs as lifestyle choices aligned with sustainable living. Corporate buyers also integrate EVs into fleets to meet sustainability targets and enhance brand reputation. This cultural shift, supported by eco-friendly values, strengthens long-term market growth. Consumer-driven sustainability ensures demand continues even beyond financial incentives, reinforcing a steady expansion of the EV ecosystem.
Key Trends & Opportunities
Corporate Fleet Electrification
Fleet electrification presents a significant opportunity in the Netherlands EV Market. Corporations increasingly adopt EVs to cut operational costs, comply with emission regulations, and meet environmental commitments. Leasing companies also drive this trend, offering flexible packages for businesses. With low-emission zones expanding in major cities, corporate adoption is expected to accelerate. This shift not only boosts PHEV and BEV sales but also strengthens demand for charging hubs and fleet management solutions, creating opportunities for automakers, infrastructure providers, and service companies.
- For instance, the Netherlands hosts around 180,000 public charging points, the highest number in Europe, which supports expanding corporate fleets and incentivizes adoption through improved infrastructure.
Integration of Smart and Connected Technologies
Smart technologies represent a growing trend in the Dutch EV ecosystem. Automakers are integrating advanced driver-assistance systems, AI-driven energy management, and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies. These innovations allow EVs to serve as mobile energy storage, supporting the national grid. Consumers benefit from enhanced safety, convenience, and cost savings through optimized energy use. With the Netherlands’ strong digital infrastructure, connected EV solutions are poised to grow quickly. This creates opportunities for technology providers, energy companies, and automakers to deliver innovative mobility services.
- For instance, Renault Group launched “Utrecht energized,” Europe’s first large-scale Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) car-sharing service in Utrecht. This initiative uses 50 Renault 5 E-Tech electric cars equipped with Mobilize V2G technology to feed electricity back to the grid during peak demand, supporting the city’s renewable energy system with 35% of rooftops fitted with solar panels.
Key Challenges
High Upfront Costs
Despite subsidies, the initial purchase price of EVs remains higher than conventional vehicles. Battery costs, though declining, still contribute significantly to pricing challenges. For many middle-income households, affordability limits adoption, especially for larger BEVs. This barrier impacts mass-market penetration, as buyers weigh total ownership costs against short-term expenses. While leasing and financing models provide some relief, the upfront cost challenge continues to hinder broader accessibility in the Netherlands EV Market.
Charging Network Strain
While the Netherlands boasts dense charging coverage, rising EV adoption creates pressure on infrastructure. Peak demand at public stations often leads to waiting times, especially in urban centers. Grid capacity constraints also pose challenges, as high-volume charging strains local networks. Expansion and upgrading of grid infrastructure are critical to sustain growth. Without timely investment, charging bottlenecks may undermine consumer confidence, reducing adoption rates. Efficient planning and smart grid integration are necessary to overcome this structural challenge.
Competition from Alternative Technologies
Alternative powertrain technologies pose a challenge to the Netherlands EV Market. Fuel cell vehicles and hybrid systems continue to attract niche buyers seeking greater range and flexibility. Meanwhile, ongoing advancements in synthetic fuels and biofuels offer competing pathways for decarbonization. These options may divert investment and slow full EV adoption. Automakers must balance development across multiple technologies, creating uncertainty in the market. While BEVs currently lead, competition from alternatives remains a critical barrier to achieving long-term EV dominance.
Regional Analysis
Eastern Netherlands
Eastern Netherlands held the largest share of 45% in 2024, making it the leading regional market. The dominance is supported by high urban density, extensive charging infrastructure, and strong policy implementation. Cities such as Arnhem and Nijmegen drive adoption with eco-mobility projects and green transport initiatives. The Netherlands EV Market benefits from concentrated consumer demand and corporate fleet electrification in this region. It continues to attract investment in public charging and smart grid integration. Eastern Netherlands sets the pace for national adoption trends.
Western Netherlands
Western Netherlands accounted for 32% share in 2024, driven by the economic strength of Amsterdam, Rotterdam, and The Hague. The region benefits from early technology adoption, strong municipal incentives, and a high concentration of corporate buyers. It is a hub for innovative mobility pilots and sustainable urban transport programs. The Netherlands EV Market in this region expands through partnerships between automakers, leasing firms, and local governments. Charging networks are advanced, supporting both private and commercial EVs. Western Netherlands reinforces its position as a critical growth corridor.
Northern Netherlands
Northern Netherlands represented 13% share in 2024, supported by regional policies promoting clean energy and sustainable living. Groningen plays a key role with its strong renewable energy projects, aligning EV growth with green electricity. It demonstrates rising adoption among private buyers encouraged by local incentives. The Netherlands EV Market in this region is shaped by small cities and rural areas, where public charging initiatives bridge accessibility gaps. Corporate adoption is lower but growing as logistics firms expand EV fleets. Northern Netherlands continues to evolve as a secondary growth region.
Southern Netherlands
Southern Netherlands captured 10% share in 2024, reflecting steady but slower adoption compared to other regions. Eindhoven and Maastricht anchor demand with research hubs and cross-border initiatives promoting e-mobility. It contributes to the Netherlands EV Market by integrating innovation from the automotive technology sector, especially through smart charging solutions. Private buyers are increasingly engaged due to government tax incentives and local programs. Corporate uptake grows in logistics and service fleets. Southern Netherlands remains a supportive region with potential for higher adoption.
Market Segmentations:
By Powertrain
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV)
- Others
By End User
- Private Buyers
- Corporate Buyers
By Region
- Eastern Netherlands
- Western Netherlands
- Northen Netherlands
- Southern Netherlands
Competitive Landscape
The Netherlands EV Market is highly competitive, shaped by global automakers and regional players focusing on innovation, affordability, and sustainability. Leading companies such as Volkswagen, BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Tesla, Volvo, Audi, and Skoda maintain strong positions through diverse product portfolios and significant investments in charging infrastructure partnerships. Tesla dominates the premium BEV category with advanced technology and a strong supercharger network, while Volkswagen and Volvo drive mass-market adoption with affordable and reliable models. Mercedes-Benz, BMW, and Audi strengthen their presence by offering performance-oriented EVs to affluent buyers, reinforcing the luxury segment. Geely Holding expands accessibility through cost-efficient EVs appealing to middle-income consumers. Local operators such as Dott contribute by focusing on micro-mobility solutions that complement broader EV adoption. Competitive intensity is reinforced by sustainability commitments, product innovation, and fleet electrification strategies, making the market dynamic and highly attractive for both established players and new entrants.
Shape Your Report to Specific Countries or Regions & Enjoy 30% Off!
Key Players
- Volkswagen
- BMW AG
- Mercedes-Benz
- Tesla
- Volvo
- Audi
- Skoda
- Dott
- Geely Holding
- Others
Recent Developments
- On August 14, 2025, Nio began delivering its Firefly compact EVs in the Netherlands and Norway.
- On June 4, 2025, MyWheels added 500 grid-connectable Renault EVs to its fleet to enable vehicle-to-grid (V2G) operations across the Netherlands.
- In early May 2025, VinFast partnered with LKQ Netherlands to expand its post-sales and maintenance service network, starting with nine workshops.
- On September 2, 2025, Q-Park Netherlands teamed up with GreenFlux to migrate its EV supply equipment under GreenFlux’s management system.
Report Coverage
The research report offers an in-depth analysis based on Powertrain, End User and Region. It details leading market players, providing an overview of their business, product offerings, investments, revenue streams, and key applications. Additionally, the report includes insights into the competitive environment, SWOT analysis, current market trends, as well as the primary drivers and constraints. Furthermore, it discusses various factors that have driven market expansion in recent years. The report also explores market dynamics, regulatory scenarios, and technological advancements that are shaping the industry. It assesses the impact of external factors and global economic changes on market growth. Lastly, it provides strategic recommendations for new entrants and established companies to navigate the complexities of the market.
Future Outlook
- Government policies will continue to accelerate EV adoption across private and corporate buyers.
- Expansion of fast-charging corridors will strengthen long-distance travel and reduce range concerns.
- Automakers will introduce more affordable EV models to target middle-income households.
- Fleet electrification programs will grow as corporations align with sustainability goals.
- Integration of smart grid and vehicle-to-grid solutions will enhance energy efficiency.
- Luxury EV demand will rise, supported by innovation in performance and design.
- Local mobility operators will expand micro-mobility EV options in urban centers.
- Consumer preference for zero-emission mobility will remain a strong growth driver.
- Cross-border cooperation with neighboring countries will support infrastructure development.
- Partnerships between automakers and energy companies will shape future charging ecosystems.





